Usage
Redirects module
Access the redirects module in the TYPO3 backend under Site Management > Redirects.
Open Redirects module
List
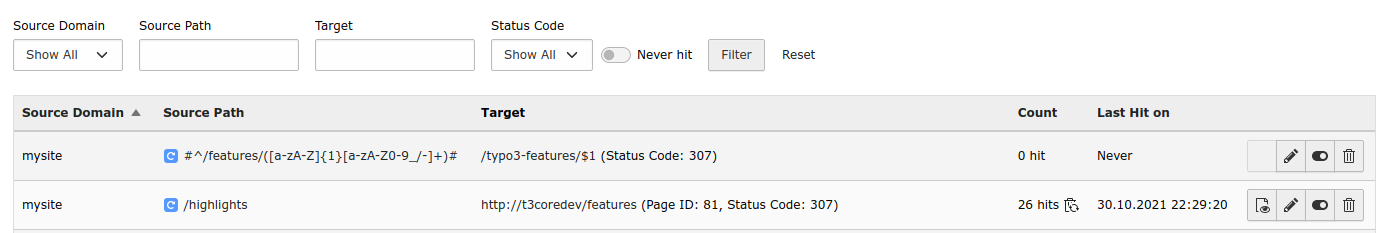
Redirect list
You will see a list of the existing redirects with the following columns labels.
- Source Domain
- Source Path
- Target
- Count: Number of "hits" (only if hit counter is on)
- Last Hit on: When was the most recent redirect "hit" (only if hit counter is on)
- Action buttons: View page, edit, disable and delete

Tip
Hover over the text to see the link markup (underline) and a tooltip.
It is also possible to sort by clicking on the Source Host or Source Path column headers and changing the sort order by clicking again, as also done elsewhere in the backend.
By clicking on the Source Path of one of the columns or on the pencil edit
icon  , you can edit the record. Clicking on a link in the
Destination column, should open the link target.
, you can edit the record. Clicking on a link in the
Destination column, should open the link target.
The + sign on the top will open an edit form to create a new redirect.
It is also possible to filter, e.g. by the Source Path, Status Code or only show redirect records which were "Never hit" (see Information on Hit counter which must be explicitly enabled via Feature Toggle).
Edit form
When creating a new redirect or editing an existing one, the edit form will open.
A redirect generally consists of these 2 parts which are separated in the edit form:
- A source part (host, path, query parameters) which is matched against the URL. If it matches, the redirect is applied
- A target part which defines where the redirect should redirect to and some additional parameters like the HTTP status code, whether to force HTTPS and keep query parameters
Also, the redirect has some additional parameters that are specific for the redirect record but not relevant when generating the redirect, such as the Protected field.
Admin users will see the respective database fields from the table
sys_ in square brackets (e.g.
Source Domain [source_host]) next to the label if in debug mode.
Non-admin users may not see all the fields. By default Source Domain, Source Path and Target are enabled, the rest are exclude fields and must be enabled in the backend group permissions, see backend user configuration.
General tab
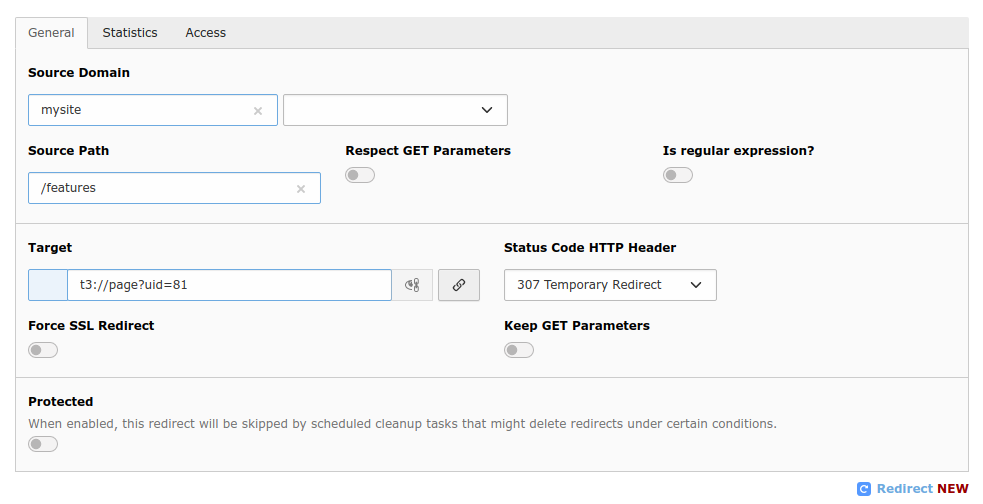
Edit redirect
Source:
Source Domain
-
- Field
-
source_host
It is possible to select one of the domains from the site configuration or use the wildcard (
*). In this case the redirect applies to all sites!
Source Path
-
- Field
-
source_path
Can be an actual path, e.g.
/path. For URLs with different entry points for languages, you should use the full path, e.g./en/. Regular expressions are possible, but thenpath is_must be enabled. Regular expressions must be enclosed in delimiters, e.g.regexp #^/orpath/ ( [a- z A- Z] {1} [a- z A- Z0- 9_/-]+)# /^\/.path\/ ( [a- z A- Z] {1} [a- z A- Z0- 9_/-]+)/
Respect GET Parameters
-
- Field
-
respect_query_parameters
If on, matching is also performed on query parameters. If off, matching is only performed on the path.
Is regular expression?
-
- Field
-
is_regexp
Evaluate the Source Path as regular expression.
Target:
Target
-
- Field
-
target
The redirect target, can be a
- path, e.g.
/features - URL, e.g.
https://example. org/ features - page ID or page URI, e.g.
t3://page?uid=1 - file URI, e.g.
t3://file?uid=1 - path with reference to
regular expression capturing group if the regular
expression feature is used with e.g. capturing groups in Source Path, e.g.
/newpath/$1
Status Code HTTP Header
-
- Field
-
target_statuscode
The HTTP status code that will be sent to the client. This is 307 (Temporary Redirect) by default.
Force SSL Redirect
-
- Field
-
force_https
When redirecting, use HTTPS when constructing the target URL. This will even be the case, if a full URL is given as target (e.g.
http://) or if the entry point of a site uses HTTP, so make sure your site supports HTTPS (which is recommended anyway).example. com/ features
Keep GET Parameters
-
- Field
-
keep_query_parameters
When redirecting, add query parameters of original URL (with possible changes) to the target. By default, the query parameters are omitted, so source URL
https://would be redirected toexample. com/ features?abc=1 https://. If there are already query parameters in the target field, these are used instead.example. com/ all- features
Protected
-
- Field
-
protected
This does not affect the redirect itself. It protects the record from automatic deletion (e.g. with redirects:cleanup).
Statistics tab
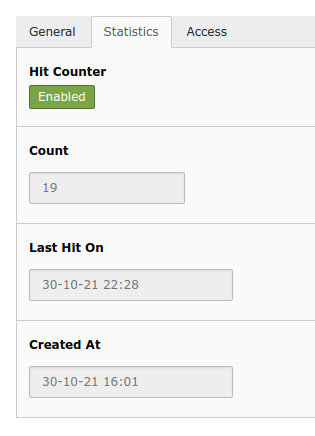
Statistics tab with hit counter
This tab is only available, if the hit counter is enabled. Here you can disable the hit counter for a specific redirect and also see read-only statistics.
Hit Counter
-
- Field
-
disable_hitcount
Disable the hit counter only for this redirect.
Count
-
- Field
-
hitcount
- Editable
-
read only
Number of hits for this particular redirect. (How often was the page accessed which triggered this redirect?)
Last Hit on
-
- Field
-
lasthiton
- Editable
-
read only
When was the last hit on this redirect?
Created At
-
- Field
-
createdon
- Editable
-
read only
When was this redirect created?
Access tab
Enabled
-
- Field
-
disabled
If disabled, the redirect has no effect.
Start
-
- Field
-
starttime
If this is not empty, "now" (current time) must be after Start time for the redirect to have effect.
Stop
-
- Field
-
endtime
If this is not empty, "now" (current time) must be before Stop time for the redirect to have effect.
Regex examples
Example 1: Source path with regular expression and capturing group
redirect
| Source Path | Is Regular Expression | target |
#^/ | true | https:// |
with the following result:
| URL | result URL |
https:// | https:// |
Example 2: Source path with regular expression, capturing group and relative target
redirect
| Source Path | Is Regular Expression | target |
#^/ | true | /newpath/$1 |
with the following result:
| URL | result URL |
https:// | https:// |
Using a relative target is necessary if a redirect must work on multiple domains or multiple environments.
Important
TYPO3 will not syntax check the redirect. Make sure you enter working redirects enclosed in delimiters. Use tools like https://regex101.com/, if necessary.
Automatic redirects creation
Redirects are created automatically on slug changes, if EXT:redirects is installed and automatic creation is enabled in site configuration.
A redirect from the old URL to the new URL will be created. All sub pages are checked too and the slugs will be updated and redirects will be created for these as well.
After the creation of the redirects a notification will be shown to the user.
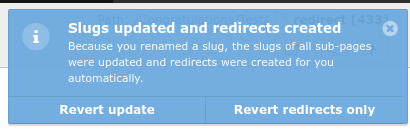
Revert redirect
The notification contains two possible actions:
- revert the complete slug update and remove the redirects
- or only remove the redirects
Note
No redirects are generated for workspace versions in the TYPO3 backend.
The setting redirect. is internally disabled in this
case.
