Configuration
Target group: Developers, Integrators
TypoScript Settings
There are a couple of TypoScript settings that can influence the output regarding search engine optimization.
Site configuration
From version 9 of TYPO3, the configuration of sites is done with the Site Management module. As the settings for your websites are important for SEO purposes as well, please make sure you check the following fields.
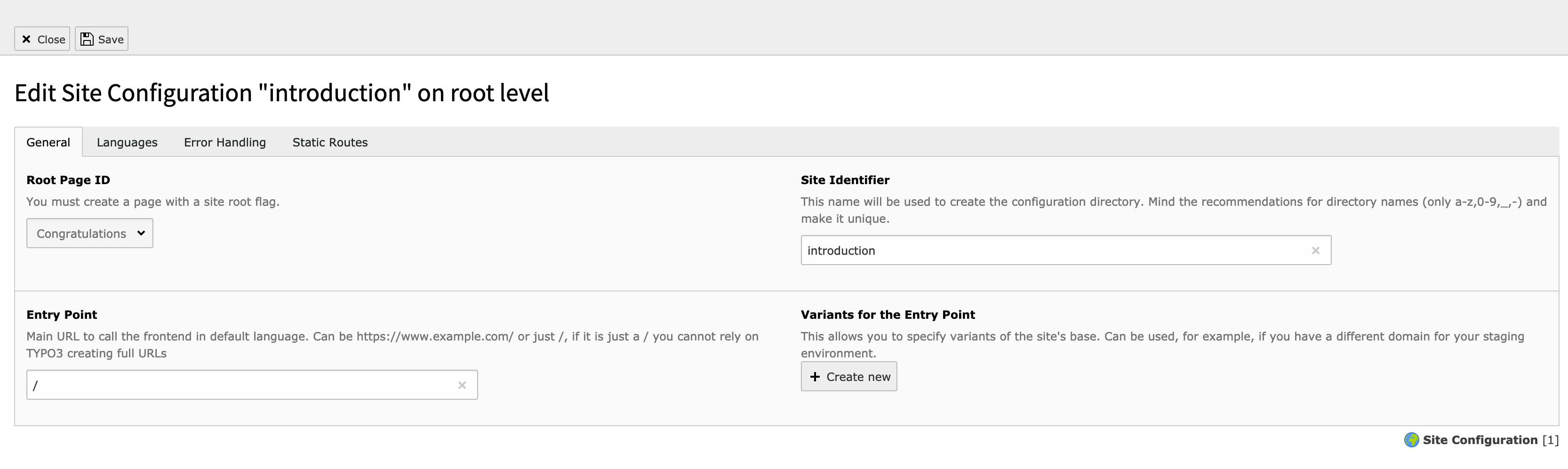
Example site
To get more in depth information about the site handling please refer to the Site handling docs.
Domains
Please ensure, that you have configured your sites so that they all have an entry point. This is used for generating the canonical tags, for example.
Warning
Please be aware that for SEO purposes it is best practise to use a fully qualified domain (for example: https://www.example.com). Therefor we don't support the SEO enhancements in TYPO3 without a full domain. It might work, but it is not officially supported.
Language
Ensure, that you setup the languages correctly. All languages should have the right information in the Locale and Language Tag field. When set correctly, TYPO3 will automatically connect your page in the different languages for search engines. This it to ensure that the search engine knows which page to show when someone is searching in a specific language.
Hint
Even if you have only one language, make sure your Locale and Language Tag fields are set correctly. Giving wrong information to search engines will not help you to rank higher.
See Adding Languages for more details.
Error pages
Although TYPO3 will respond with a HTTP status code 404 (Not found) when a page is not found, it is best practise to have a proper message telling the user that the page they requested is not available and to guide them to another page or for example to a search function of your website.
See Error handling for more details.
robots.txt
The robots.txt is a powerful tool and should be used with care. It will deny or allow search engines to access your pages. By blocking access to your pages, search engines won't crawl these pages. You should make sure that this will not prevent the search engines from finding important pages.
It is best practise to keep your robots.txt as clean as possible. An example of a minimal version of your robots.txt:
# This space intentionally left blank. Only add entries when you know how powerful the robots.txt is.
User-agent: *On Static routes you can find more details on how to create a static route that will show this information when visiting https://www.example.com/robots.txt.
When you want to disallow specific URLs, you can use the Index this page option in the backend or set the robot HTTP
header X- manually.
Redirects
Having correct redirects and choosing the appropriate status code is a very important part of SEO.
It is possible to manage redirects via the TYPO3 redirects extension, but it is not the only option and from a performance perspective it may not be the best solution. Please also see Performance in the EXT:redirects documentation.
Tags
Hreflang Tags
The generation of the <link rel="alternate" hreflang="" href="" />
tags is done automatically if the page is available in other languages.
This feature should work correctly in almost all cases.
TYPO3 is using PSR-14 events to handle the generation of those hreflang tags.
If, for some reason, you would like to alter or remove the automatically generated
tags, you can register your own EventListener. This EventListener should listen
to the \TYPO3\ event. Just make
sure your EventListener is ordered after the \TYPO3\
listener.
More information how to work with EventListeners can be found in the documentation of Event dispatcher (PSR-14 events)
Canonical Tag
Just like the hreflang tags, the <link rel="canonical" href="" /> tag is also generated automatically.
If you have a specific edge case, and you don't want TYPO3 to render the tag, you can disable rendering completely.
You just have to put this line in the ext_ of an extension and make sure your extension is loaded after EXT:seo.
unset($GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SC_OPTIONS']['TYPO3\CMS\Frontend\Page\PageGenerator']['generateMetaTags']['canonical']);Working links
Links in your website are quite important. You can use third party applications to check all your links, but you can also use the core extension linkvalidator to ensure, all the links in your site are working as expected.
Please check the documentation of TYPO3 Link Validator .
TypoScript examples
This section will provide you examples on how to configure several behaviours in the frontend.
Setting missing OpenGraph tags
Most of the OpenGraph tags are rendered automatically when EXT:seo is installed. If you want to add other fields as og:title, og:description and og:image, you can use some TypoScript code like this:
page {
meta {
og:site_name = YOUR_SITE_NAME
og:site_name.attribute = property
og:locale = en_US
og:locale.attribute = property
og:locale:alternate {
attribute = property
value {
1 = de_DE
}
}
}
}Setting fallbacks for meta tags
As you can see on TypoScript and PHP the tags are first set by PHP and after that the TypoScript config is handled. As EXT:seo is only adding the meta tags for the SEO and Social Media fields if they are filled in the page properties, you have some possibilities to add fallbacks.
Because the EXT:seo is handling the tags by PHP, you are able to add those fallbacks by TypoScript. You can just add those tags by TypoScript and those will only be rendered when EXT:seo will not render it.
An example to set a fallback description and og:description:
page {
meta {
description = Your fallback description tag
og:description = Your fallback OG:description tag
}
}Hint
Having fallbacks for those fields seems to be a good idea, but please consider if you really want those fallbacks. Those meta tags should tell search engines or social networks, what the page is about. Social networks also have their own fallbacks. Setting a fallback for og:description to the description field might not be needed as the social networks have such a fallback as well. So please consider if you want to add those tags if they does not bring additional information.
Setting fallbacks for og:image and twitter:image
If you want to have a fallback og:image or twitter:image, you can use this little snippet.
page {
meta {
og:image.stdWrap.cObject = TEXT
og:image.stdWrap.cObject {
if.isFalse.field = og_image
stdWrap.typolink {
parameter.stdWrap.cObject = IMG_RESOURCE
parameter.stdWrap.cObject.file = EXT:your_extension/Resources/Public/Backend/OgImage.svg
returnLast = url
forceAbsoluteUrl = 1
}
}
twitter:image.stdWrap.cObject = TEXT
twitter:image.stdWrap.cObject {
if.isFalse.field = twitter_image
stdWrap.typolink {
parameter.stdWrap.cObject = IMG_RESOURCE
parameter.stdWrap.cObject.file = EXT:your_extension/Resources/Public/Backend/TwitterCardImage.svg
returnLast = url
forceAbsoluteUrl = 1
}
}
}
}More information about the Meta Tag Api can be found on:
- PHP MetaTag API
- TypoScript meta
Setting defaults for the author on meta tags
This example shows how to set a default author based on the TypoScript constant {$my.:
page {
meta {
author = {$my.default.author}
}
}