Configuration
Target group: Developers, Integrators
See also
General SEO recommendations for TypoScript and Site Configuration can be found in TYPO3 explained, Suggested configuration options for improved SEO in TYPO3.
Subpages
Site sets
Include the site set "SEO Sitemap", typo3/ via the site set in the site
configuration or the custom
site package's site set.
Settings for the included set can be adjusted in the Settings editor.
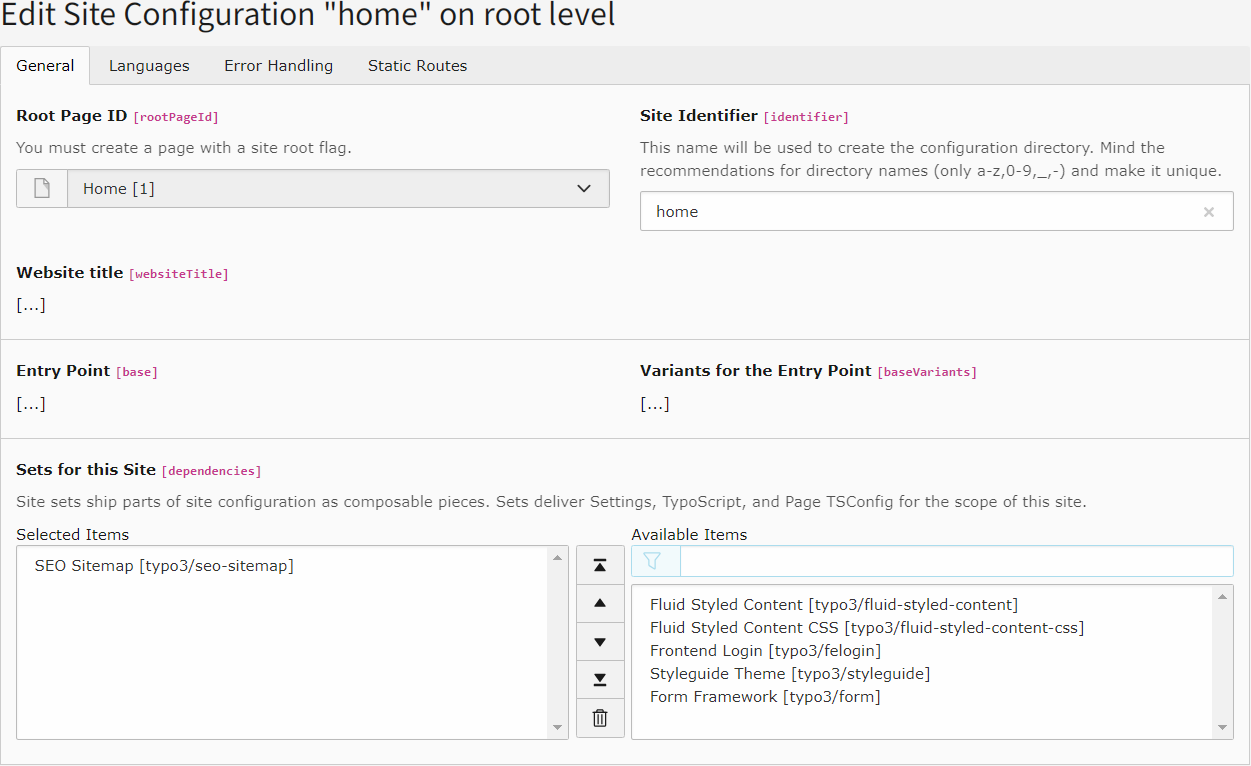
Add the site set "SEO Sitemap"
This will change your site configuration file as follows:
config/sites/my-site/config.yaml (diff)
base: 'https://example.com/'
rootPageId: 1
dependencies:
- typo3/fluid-styled-content-css
+ - typo3/seo-sitemap
If your site has a custom site package, you can also add the "SEO Sitemap" set as dependency in your site's configuration:
EXT:my_site_package/Configuration/Sets/MySite/config.yaml (diff)
