Editors Manual¶
Target group: Editors
General information on data generation¶
The extension currently supports the GPT-3.5 models. Based on your individual requirements, different models can lead to different results (also in terms of quality). In addition, other parameters can be modified to further specify the OpenAI requests. You have the possibility to adjust the different models as well as the most of the supported request parameters (detailed explanation can be found here) in the extension settings.
Generate meta description (suggestions)¶
Added an additional button next to the meta description text field. When you click this button, the (text) content of the selected page is generated, and you get meta description suggestions with the help of the AI. By default, the extension prepares the meta description suggestions in such a way that they can be selected via radio button. If you change the prompt prefix and no bullet point list is returned as a result, display problems can occur here. If you set the option showRawMetaDescriptionSuggestions to true within the extension configuration you can output the raw content and select your favorite meta description via copy/paste.
It can happen that the AI returns texts that exceed the maximum allowed length of the meta description. To additionally check the length of the meta description, the extension Yoast SEO for TYPO3 can be used, for example, or various online tools.
Generate keywords¶
Added an additional button next to the keywords text field. When you click this button, the (text) content of the selected page is generated and keywords that is as suitable as possible is created with the help of the AI. Currently, the page must not be deactivated in the backend. Depending on the page size, the process may take a few seconds. However, notifications are used to display appropriate information.
Generate page title (suggestions)¶
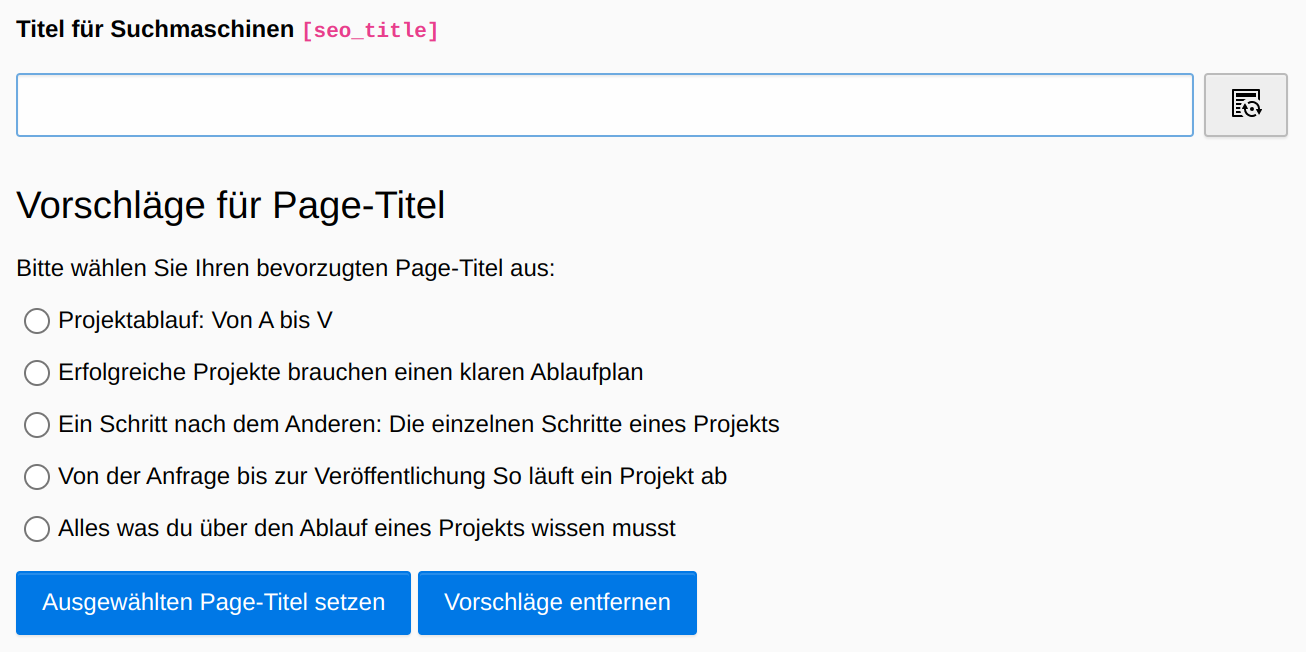
Added an additional button next to the seo title text field. When you click this button, the (text) content of the selected page is generated and you get page title suggestions with the help of the AI. By default, the extension prepares the page title suggestions in such a way that they can be selected via radio button. If you change the prompt prefix and no bullet point list is returned as a result, display problems can occur here. If you set the option showRawPageTitleSuggestions to true within the extension configuration you can output the raw content and select your favorite page title via copy/paste.
Getting results in two different ways¶
Since version 0.3.0 you have two different options to generate the desired data. Both variants adds a ["language suffix"](#how-is-the-language-suffix-determined) to get the response in the language of the analyzed page/content.
Analyzing the page content based on the text¶
If the content length does not exceed the maximum number of allowed characters (can be set in the extension settings with the option maxAllowedCharacters) and the maximum number of allowed OpenAi tokens (currently 4096 tokens per request), you can generate the desired data based on the page content in text form. If the page content exceeds the maximum allowed character length, the variant via URL is automatically used.
As already mentioned, this option is primarily limited by the length of the allowed characters per OpenAI request. Furthermore, using this method requires the use of a comparatively large number of tokens.
The following settings are necessary:
disable the useUrlForRequest option in the extension settings (as already mentioned, will be ignored if content is too large)
check if the ISO code(s) of the language configurations is/are present in the predefined fields (if not present, custom languages can be added, see Add custom languages).
Definition of the corresponding prompt in English.
The entire prompt is then assembled from the prompt prefix (from the extension settings), the page url and the language suffix (based on the language used on the page). An example of the generated prompt for page title suggestions would look like this (for a German language site):
Suggest page title ideas in bullet point list for the following text (content from extension setting openAiPromptPrefixPageTitle)
in German (language suffix based on the language used on the page)
Here comes the page content
Complete:
Suggest page title ideas in bullet point list for the following text in German:
Here comes the page content
Analyzing the page content by URL¶
In contrast to the text-based variant, this option uses the URL of the page to analyze the desired data. If you want to use this variant, the following settings are necessary:
enable the useUrlForRequest option in the extension settings
check if the ISO code(s) of the language configurations is/are present in the predefined fields (if not present, custom languages can be added, see Add custom languages).
Definition of the corresponding prompt in English.
The entire prompt is then assembled from the prompt prefix (from the extension settings), the page url and the language suffix (based on the language used on the page). An example of the generated prompt for page title suggestions would look like this (for a German language site):
Suggest page title ideas in bullet point list for (content from extension setting openAiPromptPrefixPageTitle)
https://www.example.de/ (page url)
in German (language suffix based on the language used on the page)
Complete:
Suggest page title ideas in bullet point list for https://www.example.de/ in German
Requirement is that the page is publicly accessible (hidden pages fail and pages in a local environment lead to poor results).
A major advantage is that this variant saves quite a lot of OpenAI tokens (and thus costs), since only the URL is sent to OpenAI instead of the entire page content
How is the language suffix determined?¶
The root page of the page to be analyzed is determined. Based on this, the ISO code used (the iso-639-1 field of the corresponding language from `config.yaml) is determined. The corresponding language has already been created for the conventional ISO codes. The following ISO codes and languages are already stored:
'en' => 'English',
'us' => 'English',
'gb' => 'English',
'de' => 'German',
'at' => 'German',
'ch' => 'German',
'fr' => 'French',
'nl' => 'Dutch',
'be' => 'Belgian',
'es' => 'Spanish',
'pl' => 'Polish',
'cz' => 'Czech',
'sk' => 'Slovak',
'si' => 'Slovenian',
'ro' => 'Romanian',
'ua' => 'Ukrainian',
'it' => 'Italian',
'se' => 'Swedish',
'no' => 'Norwegian',
'fi' => 'Finnish',
'dk' => 'Danish',
'jp' => 'Japanese',
'cn' => 'Chinese'
Add custom languages¶
If the desired ISO code and language is not contained, it can be created using a data record "Custom language". The user-defined languages are added automatically (already existing languages are replaced by user-defined languages).
