Attention
TYPO3 v6 has reached its end-of-life April 18th, 2017 and is not maintained by the community anymore. Looking for a stable version? Use the version switch on the top left.
There is no further ELTS support. It is strongly recommended updating your project.
Translating XLIFF files¶
This sections highlights the different ways to translate XLIFF files.
The TYPO3 translation server¶
The TYPO3 community manages an official translation server, running Pootle. Localization files in English are uploaded on that server and translations are packaged nightly. They are fecthed in the TYPO3 CMS backend, via the Extension Manager (or the new "Language" module since version 6.0).
It is not the point of this manual to go into the details of the translation process. More information can be found in the TYPO3 wiki.
Translating locally¶
Using Poedit or Virtaal, it is possible to translate XLIFF files locally. Both are open source, cross-platform applications.
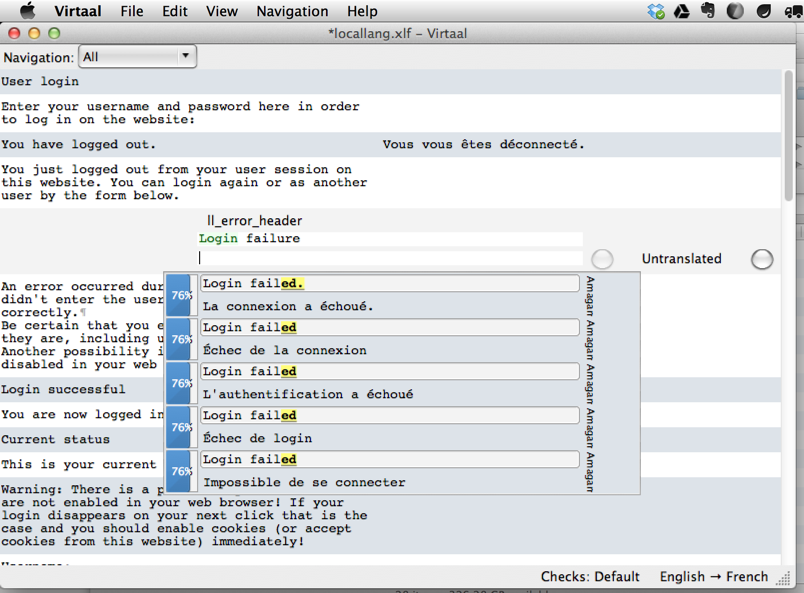
Translating with Virtaal, with suggestions from other software¶
Translating files locally is useful for extensions which are not meant to be published or for creating custom translations.
Custom translations¶
The $GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['locallangXMLOverride'] allows to
override both locallang-XML and XLIFF files. Actually this is not just about translations.
Default language files can also be overridden. In the case of XLIFF files, the
syntax is as follows (to be placed in an extension's ext_localconf.php file):
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['locallangXMLOverride']['EXT:cms/locallang_tca.xlf'][] = 'EXT:examples/Resources/Private/Language/custom.xlf';
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['locallangXMLOverride']['de']['EXT:cms/locallang_tca.xlf'][] = 'EXT:examples/Resources/Private/Language/de.custom.xlf';
The first line shows how to override a file in the default language, the second how to override a German ("de") translation. The German language file looks like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" standalone="yes" ?>
<xliff version="1.0">
<file source-language="en" datatype="plaintext" original="messages" date="2013-03-09T18:44:59Z" product-name="examples">
<header/>
<body>
<trans-unit id="pages.title_formlabel" xml:space="preserve">
<source>Most important tile</source>
<target>Wichtigster Titel</target>
</trans-unit>
</body>
</file>
</xliff>
and the result can be easily seen in the backend:
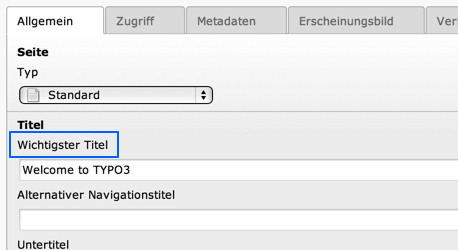
Custom translation in the TYPO3 backend¶
Important
Please note that you do not have to copy the full reference file, but only the labels you want to translate.
The path to the file to override must be expressed as
EXT:foo/bar/.... For the extension "xlf" or "xml" can be used interchangeably. The TYPO3 Core will try both anyway, but using "xlf" is more correct and future-proof.The files containing the custom labels must be located inside an extension. Other locations will not be considered (this is a bug, but must be taken as a constraint for now).
Custom languages¶
Going further it is even possible - since TYPO3 CMS 4.6 - to add custom languages to the TYPO3 backend and create the translations locally using XLIFF files.
First of all, the language must be declared:
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['localization']['locales']['user'] = array(
'de_CH' => 'Swiss German',
);
This new language does not need to be entirely translated. It can be defined as falling back to another language, so that only differing labels need be translated:
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['localization']['locales']['dependencies'] = array(
'de_CH' => array('de_AT', 'de'),
);
In this case we define that "de_CH" can fall back on "de_AT" (another custom translation) and then on "de".
The translations have to be stored in the appopriate folder, in this case
typo3conf/l10n/de_CH.
The very least you need is to translate the label containing the name of the
language itself, so that it appears in the user preferences. In our example
this would be in file typo3conf/l10n/de_CH/setup/mod/de_CH.locallang.xlf.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<xliff version="1.0">
<file source-language="en" target-language="de_CH" datatype="plaintext" original="messages" product-name="setup">
<header/>
<body>
<trans-unit id="lang_de_CH" approved="yes" xml:space="preserve">
<source>Swiss German</source>
<target state="translated">Swiizertütsch</target>
</trans-unit>
</body>
</file>
</xliff>
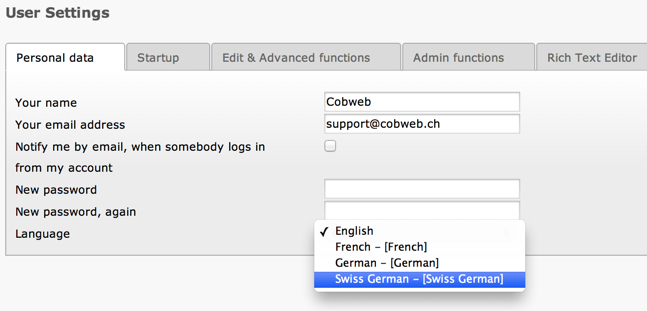
The new language appears in the user preferences¶
Note
Any language will always fall back on the default one (i.e. English) when a translation is not found. A custom language will fall back on its "parent" language automatically. Thus - in our example - no fallback would have to be defined for "de_CH" if it were just falling back on "de".
Custom translation servers¶
With the use of XLIFF and the freely available Pootle translation server, companies and individuals may easily set up a custom translation server for their extensions.
There is a signal that can be caught to change the translation server URL to use. The first
step is to register one's code for handling the signal. Such code would be placed in an
extension's ext_localconf.php file:
$signalSlotDispatcher = \TYPO3\CMS\Core\Utility\GeneralUtility::makeInstance('TYPO3\\CMS\\Extbase\\SignalSlot\\Dispatcher');
$signalSlotDispatcher->connect(
'TYPO3\\CMS\\Lang\\Service\\UpdateTranslationService',
'postProcessMirrorUrl',
'Company\\Extension\Slots\\CustomMirror',
'postProcessMirrorUrl'
);
The class (slot) which receives the signal (EXT:myext/Classes/Slots/CustomMirror.php)
could look something like:
<?php
namespace Company\Extensions\Slots;
class CustomMirror {
/** @var string */
static protected $extKey = 'myext';
public function postProcessMirrorUrl($extensionKey, &$mirrorUrl) {
if ($extensionKey === self::$extKey) {
$mirrorUrl = 'http://mycompany.tld/typo3-packages/';
}
}
}
Note that the mirror URL is passed as a reference, so that it can be modified. In the above example, the URL is changed only for a given extension, but of course it could be changed on a more general basis.
On the custom translation server side, the structure needs to be:
https://mycompany.tld/typo3-packages/
`-- <first-letter-of-extension-key>
`-- <second-letter-of-extension-key>
`-- <extension-key>-l10n
|-- <extension-key>-l10n-de.zip
|-- <extension-key>-l10n-fr.zip
|-- <extension-key>-l10n-it.zip
`-- <extension-key>-l10n.xml
hence in our example:
https://mycompany.tld/typo3-packages/
`-- m
`-- y
`-- myext-l10n
|-- myext-l10n-de.zip
|-- myext-l10n-fr.zip
|-- myext-l10n-it.zip
`-- myext-l10n.xml
And the myext-l10n.xml file contains something like:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes" ?>
<TERlanguagePackIndex>
<meta>
<timestamp>1374841386</timestamp>
<date>2013-07-26 14:23:06</date>
</meta>
<languagePackIndex>
<languagepack language="de">
<md5>1cc7046c3b624ba1fb1ef565343b84a1</md5>
</languagepack>
<languagepack language="fr">
<md5>f00f73ae5c43cb68392e6c508b65de7a</md5>
</languagepack>
<languagepack language="it">
<md5>cd59530ce1ee0a38e6309544be6bcb3d</md5>
</languagepack>
</languagePackIndex>
</TERlanguagePackIndex>
