Indexing
ke_search fetches content from pages, news, files etc. and stores it into an index table. This process is called "indexing". For each content type (pages, news etc.) ke_search needs an "indexer" (see below, Available indexers).
Whenever the content in your website changes, the indexing process needs to be started to reflect that changes in the search results.
Create indexer configurations
You will have to create an indexer configuration for each content type you want to index (pages, news, ...). You may create more than one indexer configuration of one type, eg. two page indexer configurations for different page trees.
Use the list module an open your search storage page and create an "indexer configuration" record.
Configure the indexer configuration
- Set the title, this field is used only internally.
- Set the storage page for the index. Set this page to your search storage folder.
- If you are working with filters, you can define that every index entry gets a tag automatically if it has been indexed by this indexer by setting Add tag to all indexed elements to a filter option you like. By doing so you can for example create a filter by content type (news, page, event, ...) if you have an indexer for each content type. Please remember that you will have to create the filter options first.
The other indexer configurations options differ from type to type.
Full indexing and incremental indexing
Since version 3.8.0 there are two ways of indexing the data: full and incremental.
Note
Incremental indexing is a lot faster than full indexing!
Full indexing goes through all the data which should be indexed (records, files, custom indexers) and checks for each record if it has been changed or if it is new. In this case the data will be updated or stored to the index. After that a cleanup process is started and all old data will be deleted.
The incremental indexing process fetches only the records which have been added, changed or deleted since the last indexing process took place. It only adds, updates or deletes those records from the index.
Incremental indexing has a few drawbacks:
- Not every indexer has incremental indexing capabilities. The indexer class needs to implement the method startIncrementalIndexing. If this method does not exist, a full indexing is started for this indexer even if the indexing process is started in incremental mode. Since there is no cleanup in incremental mode, old entries won't be deleted in incremental mode if the indexer does not support incremental indexing. The indexing report will mention if no incremental indexing is available ("Incremental indexing is not available for this indexer, starting full indexing.")
- Changes to files won't be recognized if you use the page or content element indexer, only if you use the dedicated file indexer.
Therefore it is recommended to run the full indexing process once in a while (like once a day or once a week) and run the incremental indexer more often (like once an hour). You can do so by creating two scheduler tasks, one for the full indexing and one for the incremental indexing.
After adding or removing an indexer configuration you should always run a full indexing process.
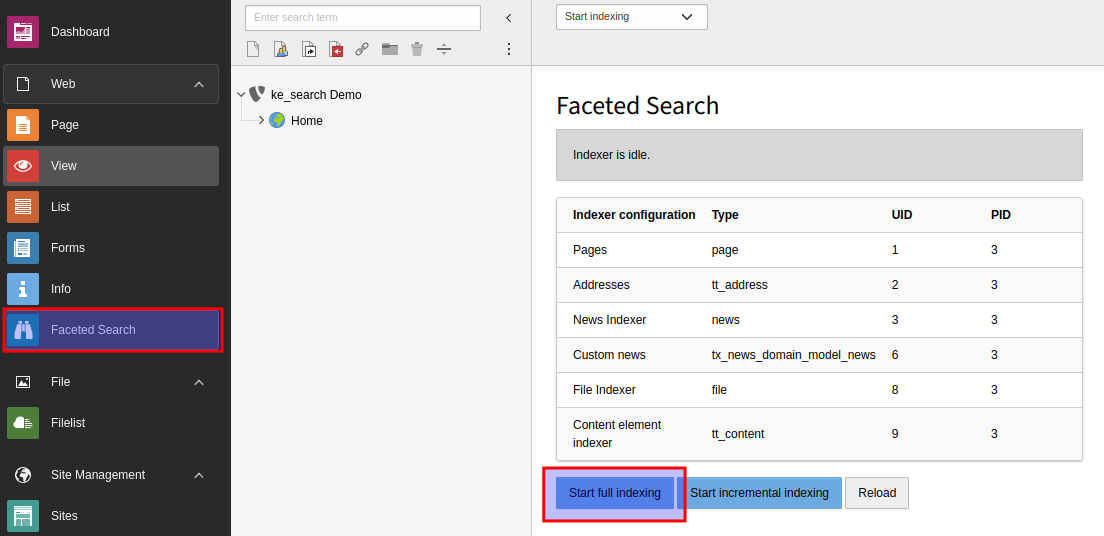
Starting the indexing process manually
You can start the indexing process in the Faceted Search backend module.
You can also start the indexer using the command line
vendor/bin/typo3 ke_search:indexingOr if you want to use the incremental mode
vendor/bin/typo3 ke_search:indexing --indexingMode=incrementalStarting the indexing process automatically
For keeping the index up-to-date it is recommended to use the TYPO3 scheduler.
You can execute the console command via scheduler.
- Create a task, choose "Execute console commands".
- Choose
ke_in the dropdown Schedulable command.search: indexing - After saving the form you can choose whether you want to do full indexing (default) or incremental indexing by setting
the option indexingMode to either
fullorincremental. - Deactivate the Allow Parallel Execution option (default).
Available indexers
ke_search comes with indexers for the most important content types.
