Pages
The page indexer indexes standard TYPO3 pages.
All content elements on a page will be grouped and written to the index in one index entry. That means if your search word appears in two different text elements on a page, you will get only one search result for the page these two elements belong to.
There is a set of default content element types which are indexed without further configuration needed. If you created your own content elements (e.g. with EXT:mask or EXT:content_blocks) you can add them to the configuration as described below.
Configuration
- Set the type of the indexer configuration to
Pages. - Set a title (only for internal use).
- Set the field Storage to the folder where you want to store your search data.
- Set Startingpoints (recursive) to the pages you want to index recursively.
- Set Single Pages to the pages you want to index non-recursively.
Content element types
By default the page indexer indexes content element of the following types which are delivered by the TYPO3 core:
- Text (CType
text) - Text with image / Media element (CTypes
textmediaandtextpic) - Bullet list (CType
bullets) - Table (CType
table) - Plain HTML (CType
html) - Header (CType
header) - File lists (CType
uploads) - Referenced content elements (CType
shortcut)
Additionally it indexes content elements provided by the EXT:bootstrap_package:
- Accordion (CType
accordion) - Tab (CType
tab) - Carousel (CTypes
carousel,carousel_,fullscreen carousel_)small - Icon Group (CType
icon_)group - Card Group (CType
card_)group - Timeline (CType
timeline)
File indexing
Files linked in RTE text fields will be detected and indexed. Also files linked
in fields of type "link" (e.g. header_) will be detected.
Container and Gridelements
If content elements are placed inside a container or gridelement, the indexer will index these content elements as well, even if they are nested inside other containers or gridelements. If a container is inserted via the "shortcut" content element on another page, the content will be indexed as well (after version 6.3.0), but not recursively.
Abstract
In the page properties there's the field Abstract for search result in the tab Search. Here you can enter a short description of the page, this text will be used as an abstract in the search result list. If this field is empty, it falls back to the field Description in the Metadata tab of the page properties. In the FlexForm of the search plugin you can define the "Text for used for search result (preview text)" and set it to "Always show the abstract if set" or "Show abstract if it contains searchword, otherwise show an excerpt from the content".
Advanced options
- If you set Index content elements with restrictions to
yes, content elements will be indexed even if they have frontend user group access restrictions. This function may be used to "tease" certain content elements in your search and then tell the user that he will have to log in to see the full content once he clicks on the search result. - If you created custom page types which you want to index, you can add them in Page types which should be indexed set the page types you want to index.
- in Content element types which should be indexed you can add your
own content element types. For example those created with EXT:mask or
EXT:content_blocks. If you are not sure what to enter here, have a look a the
table
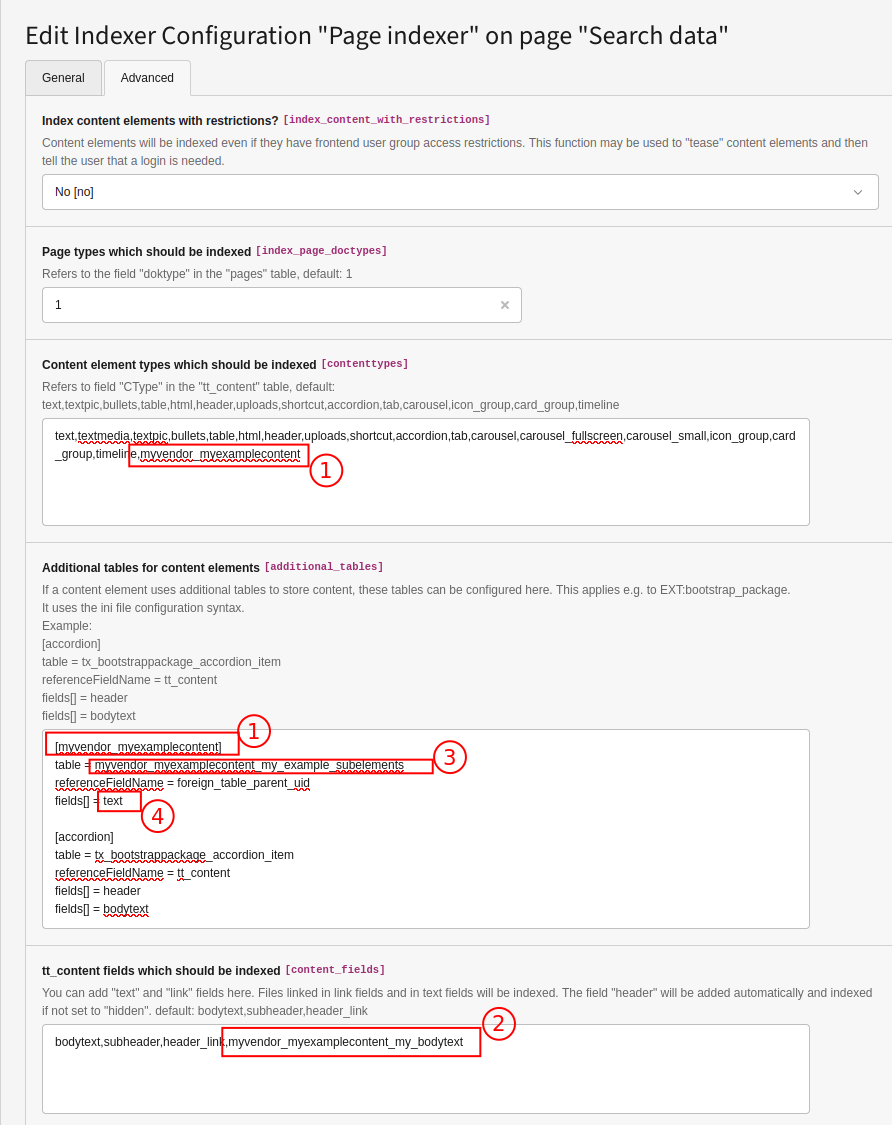
tt_in the columncontent CTypeor activate TYPO3 backend debug mode. - (since version 5.3.0) In Additional tables for content elements you can define tables which hold additional content. That is used for example by EXT:bootstrap_package, EXT:mask or EXT:content_blocks. See below ("Index content from additional tables") for details.
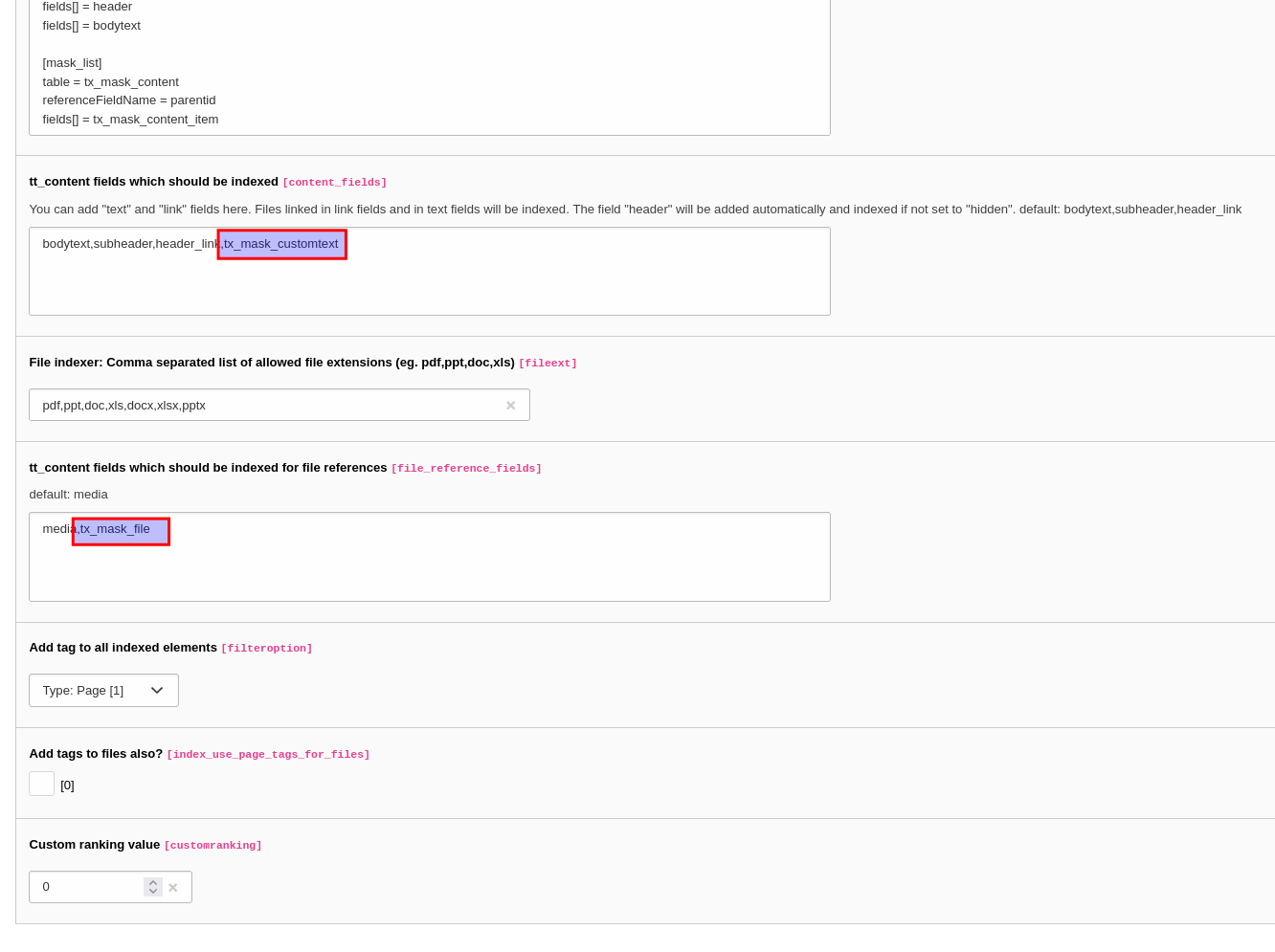
- In tt_content fields which should be indexed you can define custom fields which should be indexed. Default is here "bodytext,subheader, header_link" which is used for the default content elements. This is useful if you added your custom content elements for example using EXT:mask or EXT:content_blocks.
- Using the field Comma separated list of allowed file extensions
you can set the allowed file extension of files to index. By default this is
set to
pdf,ppt,doc,xls,docx,xlsx,pptx. For pdf, ppt, doc and xls files you need to install external tools on the server. - Using the field tt_content fields which should be indexed for file references
you can add fields from
tt_which hold file references and for which the attached files should be indexed.content - You can choose to add a tag to all index entries created by this indexer.
- You can choose to add that tag also to files indexed by this indexer.
Index content from additional tables (eg. mask, bootstrap_package, content_blocks)
Some extension
Some extension like the widely used mask and bootstrap_ and
content_ extensions store content not in the tt_content table but in
additional tables which hold a reference to the record in tt_content.
Since version 5.3.0 it is possible to index those tables without the need
for a 3rd party extension or custom indexer. In the field
Additional tables for content elements you can configure those
tables. The ini configuration format is used here.
Since version 5.6.0 / 6.1.0 it is possible to index sub-elements of additional tables. If you have repeating elements in a mask element which themselves have repeating elements you can define the parent table for the sub-elements here. Indexing will be done recursively.
You need to define the table name, the field which holds the reference to the tt_content table and the fields which should be indexed.
Options
- first line (eg.
[custom_)element] - The content type, stored as
CTypein the tablett_. You will also have to add this to Content element types which should be indexed. If your content element has multiple additional tables, you can have multiple configurations for the same CType by adding a dot and an index, e.g. "my_ctype.1", "my_ctype.2" which then will all internally be mapped to the configuration for "my_ctype".content - table
- This is the table that holds the content.
- referenceFieldName
- This is the field that holds the relation to the tt_content record (the
UID of the record). In EXT:bootstrap_package it is named
tt_, in EXT:mask it is namedcontent parentid, in EXT:content_blocks it is namedforeign_.table_ parent_ uid - parentTable
- (since version 5.6.0 / 6.1.0) The parent table is an optional setting. It's only necessary if you want to index sub-elements of EXT:mask. For example If you have repeating elements in a mask element which themselves have repeating elements. You can define the parent table for the sub-elements here (see example below). Indexing will be done recursively. If set the database query will contain a "WHERE parenttable = ..." condition. This column exists in content elements from EXT:mask but not in content elements from EXT:bootstrap_package.
- fields[]
- A list of database fields which should be indexed. If the field is
configured as type "file" in the TCA the indexer will check if it links
to a file and index that file. Otherwise the field will be treated as a
text field and will be indexed like other fields, e.g. the
bodytextfield in content elements. Links to files will also be resolved here and the files will be indexed.
Examples
Bootstrap Package
Add this to Additional tables for content elements to
index the bootstrap package element "accordion" (remember to also add
accordion to Content element types which should be indexed:
[accordion]
table = tx_bootstrappackage_accordion_item
referenceFieldName = tt_content
fields[] = header
fields[] = bodytextMask
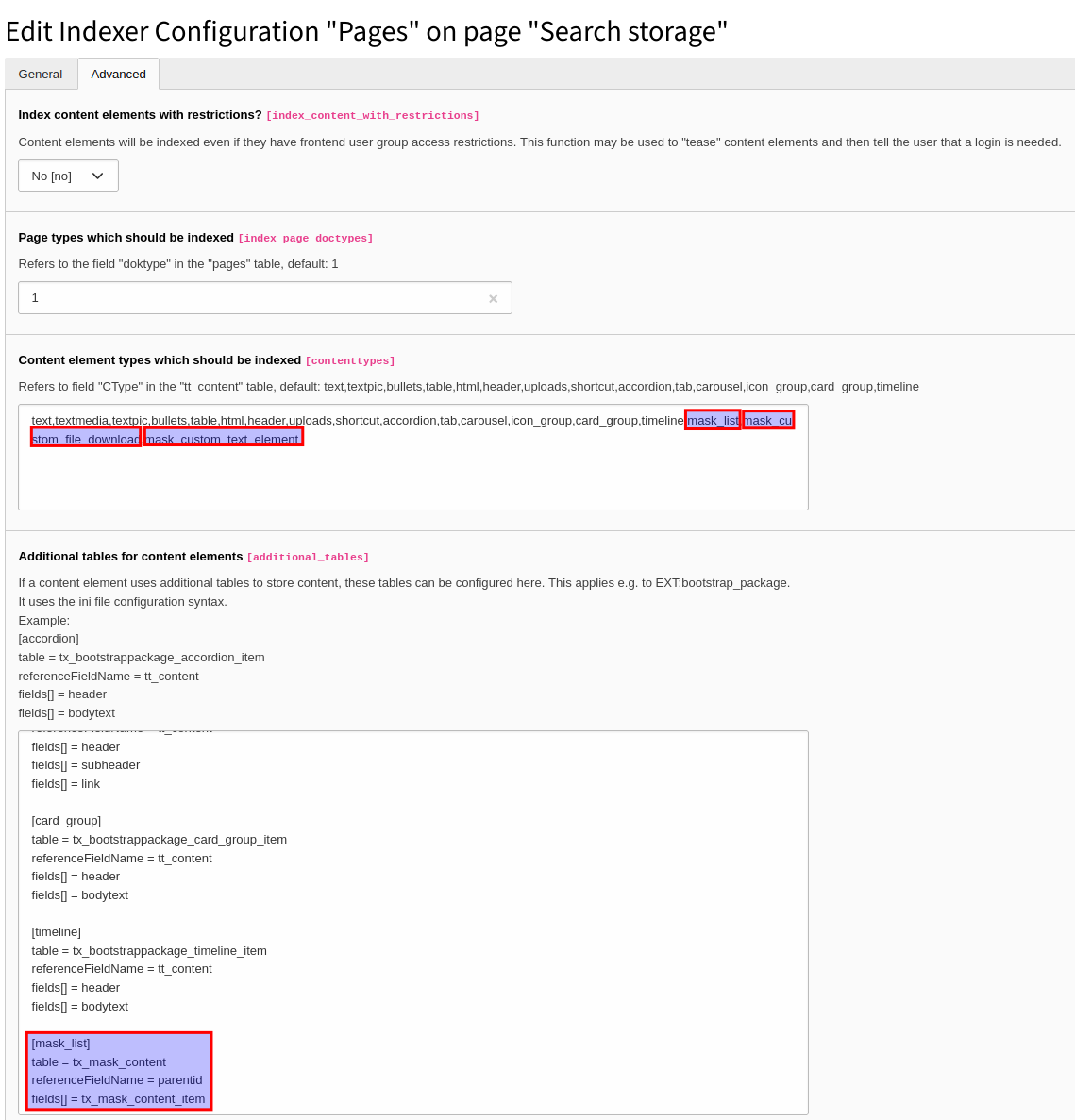
Add this to Additional tables for content elements to
index mask elements (remember to also add
mask_ and mask_ to Content element types which should be indexed:
[mask_list]
table = tx_mask_content
referenceFieldName = parentid
fields[] = tx_mask_content_itemMask with multiple additional tables
This is an example how to add multiple additional tables for the same CType.
[mask_mytest]
table = tx_mask_repeating1
referenceFieldName = parentid
fields[] = tx_mask_name
[mask_mytest.1]
table = tx_mask_repeating2
referenceFieldName = parentid
fields[] = tx_mask_titleMask with sub-elements in additional tables
This is an example how to index sub-elements of additional tables
(note the parent configuration line).
[mask_mytest]
table = tx_mask_repeating1
referenceFieldName = parentid
fields[] = tx_mask_name
[mask_mytest.1]
table = tx_mask_repeating2
parentTable = tx_mask_repeating1
referenceFieldName = parentid
fields[] = tx_mask_titleMore Mask examples
This is an example for a some mask elements:
- The element
mask_adds a fieldcustom_ text_ element tx_to themask_ customtext tt_table.content - The element
mask_adds a file download fieldcustom_ file_ download tx_to themask_ file tt_table.content - The element
mask_stores content in the tablelist tx_.mask_ content
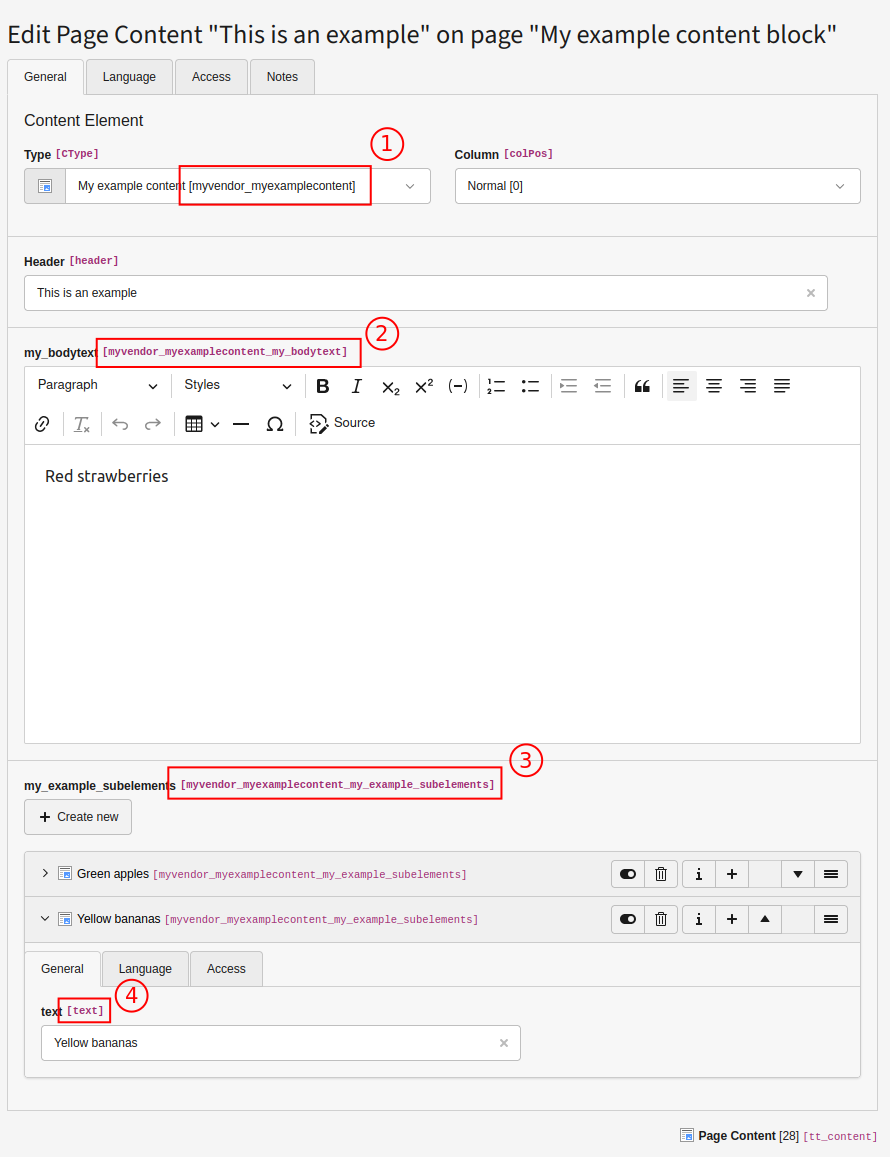
Content Blocks
In order to index content elements from EXT:content_blocks you need to add
- the name of the CType to Content element types which should be indexed.
- the name of the tt_content field to tt_content fields which should be indexed.
- (optionally) the configuration for the additional table(s) to Additional tables for content elements.
In order to find out the correct names you can activate the TYPO3 backend debug mode.