Attention
TYPO3 v9 has reached its end-of-life September 30th, 2021 and is not maintained by the community anymore. Looking for a stable version? Use the version switch on the top left.
You can order Extended Long Term Support (ELTS) here: TYPO3 ELTS.
Service API¶
All service classes must inherit from the base service class
\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Service\AbstractService,
unless the service type provides a specific
base class (authentication services, for example, inherit from
\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Authentication\AbstractAuthenticationService instead).
These specific classes should
normally themselves extend \TYPO3\CMS\Core\Service\AbstractService.
This class provides a large number of important or useful methods which are
described below, grouped by type of usage.
Service Implementation¶
These methods are related to the general functioning of services.
Important
init() and reset() are the most important methods to implement
when developing your own services.
- init
This method is expected to perform any necessary initialization for the service. Its return value is critical. It should return
falseif the service is not available for whatever reason. Otherwise it should returntrue.Note that's it's not necessary to check for OS compatibility, as this will already have been done by
\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Utility\ExtensionManagementUtility::addService()when the service is registered.Executables should be checked, though, if any.
The
init()method is automatically called by\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Utility\GeneralUtility::makeInstanceService()when requesting a service.- reset
When a service is requested by a call to
\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Utility\GeneralUtility::makeInstanceService(), the generated instance of the service class is kept in a registry ($GLOBALS['T3_VAR']['makeInstanceService']). When the same service is requested again during the same code run, a new instance is not created. Instead the stored instance is returned. At that point thereset()method is called.This method can be used to clean up data that may have been set during the previous use of that instance.
- __destruct
Clean up method. The base implementation calls on
unlinkTempFiles()to delete all temporary files.
The little schema below summarizes the process of getting a service
instance and when each of init() and reset() are
called.
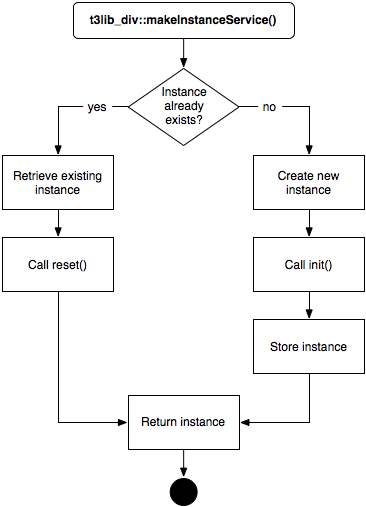
The life cycle of a service instance¶
Getter Methods for Service Information¶
Most of the below methods are quite obvious, except for
getServiceOption().
- getServiceInfo
Returns the array containing the service's properties
- getServiceKey
Returns the service's key
- getServiceTitle
Returns the service's title
- getServiceOption
This method is used to retrieve the value of a service option, as defined in the
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SVCONF']array. It will take into account possible default values as described in the Service configuration chapter.This method requires more explanation. Imagine your service has an option called "ignoreBozo". To retrieve it in a proper way, you should not access
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SVCONF']directly, but usegetServiceOption()instead. In its simplest form, it will look like this (inside your service's code):$ignoreBozo = $this->getServiceOption('ignoreBozo');
This will retrieve the value of the "ignoreBozo" option for your specific service, if defined. If not, it will try to find a value in the default configuration. Additional call parameters can be added:
the second parameter is a default value to be used if no value was found at all (including in the default configuration)
the third parameter can be used to temporarily switch off the usage of the default configuration.
This allows for a lot of flexibility.
Error Handling¶
This set of methods handles the error reporting and manages the error queue. The error queue works as a stack. New errors are added on top of the previous ones. When an error is read from the queue it is the last one in that is taken (last in, first out). An error is actually a short array comprised of an error number and an error message.
The error queue exists only at run-time. It is not stored into session or any other form of persistence.
- errorPush
Puts a new error on top of the queue stack.
- errorPull
Removes the latest (topmost) error in the queue stack.
- getLastError
Returns the error number from the latest error in the queue, or true if queue is empty.
- getLastErrorMsg
Same as above, but returns the error message.
- getErrorMsgArray
Returns an array with the error messages of all errors in the queue.
- getLastErrorArray
Returns the latest error as an array (number and message).
- resetErrors
Empties the error queue.
General Service Functions¶
- checkExec
This method checks the availability of one or more executables on the server. A comma-separated list of executable names is provided as a parameter. The method returns
trueif all executables are available.The method relies on
\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Utility\CommandUtility::checkCommand()to find the executables, so it will search through the paths defined/allowed by the TYPO3 CMS configuration.- deactivateService
Internal method to temporarily deactivate a service at run-time, if it suddenly fails for some reason.
I/O Tools¶
A lot of early services were designed to handle files, like those used by the DAM. Hence the base service class provides a number of methods to simplify the service developer's life when it comes to read and write files. In particular it provides an easy way of creating and cleaning up temporary files.
- checkInputFile
Checks if a file exists and is readable within the paths allowed by the TYPO3 CMS configuration.
- readFile
Reads the content of a file and returns it as a string. Calls on
checkInputFile()first.- writeFile
Writes a string to a file, if writable and within allowed paths. If no file name is provided, the data is written to a temporary file, as created by
tempFile()below. The file path is returned.- tempFile
Creates a temporary file and keeps its name in an internal registry of temp files.
- registerTempFile
Adds a given file name to the registry of temporary files.
- unlinkTempFiles
Deletes all the registered temporary files.
I/O Input and I/O Output¶
These methods provide a standard way of defining or getting the content that needs to be processed – if this is the kind of operation that the service provides – and the processed output after that.
- setInput
Sets the content (and optionally the type of content) to be processed.
- setInputFile
Sets the input file from which to get the content (and optionally the type).
- getInput
Gets the input to process. If the content is currently empty, tries to read it from the input file.
- getInputFile
Gets the name of the input file, after putting it through
checkInputFile(). If no file is defined, but some content is, the method writes the content to a temporary file and returns the path to that file.- setOutputFile
Sets the output file name.
- getOutput
Gets the output content. If an output file name is defined, the content is gotten from that file.
- getOutputFile
Gets the name of the output file. If such file is not defined, a temporary file is created with the output content and that file's path is returned.
