Attention
TYPO3 v11 has reached end-of-life as of October 31th 2024 and is no longer being maintained. Use the version switcher on the top left of this page to select documentation for a supported version of TYPO3.
Need more time before upgrading? You can purchase Extended Long Term Support (ELTS) for TYPO3 v11 here: TYPO3 ELTS.
Backend module API
As for frontend plugins, you can use Fluid templates to create the view and controller actions for the functionality.
Tip
The Extension Builder can be used to generate basic code for a new extension. You can also use this to create backend modules.
Adding new modules
Modules added by extensions are registered in the file ext_tables.php using the following API:
Based on Extbase:
// Module System > Backend Users
\TYPO3\CMS\Extbase\Utility\ExtensionUtility::registerModule(
'Beuser',
'system',
'tx_Beuser',
'top',
[
\TYPO3\CMS\Beuser\Controller\BackendUserController::class => 'index, show, addToCompareList, removeFromCompareList, removeAllFromCompareList, compare, online, terminateBackendUserSession, initiatePasswordReset',
\TYPO3\CMS\Beuser\Controller\BackendUserGroupController::class => 'index, addToCompareList, removeFromCompareList, removeAllFromCompareList, compare'
],
[
'access' => 'admin',
'iconIdentifier' => 'module-beuser',
'labels' => 'LLL:EXT:beuser/Resources/Private/Language/locallang_mod.xlf',
'navigationComponentId' => 'TYPO3/CMS/Backend/PageTree/PageTreeElement',
'inheritNavigationComponentFromMainModule' => false,
]
);Here the module tx_Beuser is declared as a submodule of the already existing
main module system.
Parameters:
- The first argument contains the extension name (in UpperCamelCase) or the extension key (in lower_underscore). Since TYPO3 v10.0, you should no longer prepend the vendor name here, see Deprecation: #87550 - Use controller classes when registering plugins/modules.
- Main module name, in which the new module will be placed, for example 'web' or 'system'.
- Submodule key: This is an identifier for your new module.
-
Position of the module: Here, the module should be placed at the
topof the main module, if possible. If several modules are declared at the same position, the last one wins. The following positions are possible:top: the module is prepended to the top of the submodule listbottomor empty string: the module is appended to the end of the submodule listbefore:<submodulekey>: the module is inserted before the submodule identified by<submodulekey>after:<submodulekey>: the module is inserted after the submodule identified by<submodulekey>
- Allowed controller => action combinations. Since TYPO3 v10.0 you should use fully qualified class names here, see Deprecation: #87550 - Use controller classes when registering plugins/modules.
-
Module configuration: The following options are available:
-
access: can contain several, separated by commasystemMaintainer: the module is accessible to system maintainers only.admin: the module is accessible to admins onlyuser: the module can be made accessible per usergroup: the module can be made accessible per usergroup
- Module
iconIdentifier - A language file containing
labelslike the module title and description, for building the module menu and for the display of information in the About Modules module (found in the main help menu in the top bar). TheLLL:prefix is mandatory here and is there for historical reasons. - Navigation component
navigationComponentId- you can specify which navigation component you want to use, for exampleTYPO3/for a page tree orCMS/ Backend/ Page Tree/ Page Tree Element TYPO3/for a folder tree. If you don't want to show a navigation component at all you can either set this to an empty string or not declare it at all. In case the main module (e.g. "web") has a navigationComponent defined by default you'll have to also setCMS/ Backend/ Tree/ File Storage Tree Container 'inherit.Navigation Component From Main Module' => false
-
Note
When registering frontend plugins, you must define which actions are not to be stored in the cache. This is not necessary for backend modules, because the actions are generally not being cached in the backend.
Configuration with TypoScript
Backend modules can, like frontend plugins, be configured via TypoScript. While the frontend plugins
are configured with plugin., for the configuration of the backend
module. is used.
Example for configuring the paths of Fluid files:
module.tx_example {
view {
templateRootPaths {
10 = EXT:example/Resources/Private/Backend/Templates/
}
layoutRootPaths {
10 = EXT:example/Resources/Private/Backend/Layouts/
}
}
}Without Extbase:
\TYPO3\CMS\Core\Utility\ExtensionManagementUtility::addModule(
'random',
'filerelatedmodule',
'top',
null,
[
'navigationComponentId' => 'TYPO3/CMS/Backend/Tree/FileStorageTreeContainer',
'routeTarget' => \MyVendor\MyExtension\Controller\FileRelatedController::class . '::indexAction',
'access' => 'user,group',
'name' => 'myext_file',
'icon' => 'EXT:myextension/Resources/Public/Icons/module-file-related.svg',
'labels' => 'LLL:EXT:myextension/Resources/Private/Language/Modules/file_related.xlf'
]
);Parameters:
- Main module name, in which the new module will be placed, for example 'web' or 'system'.
- Submodule key: This is an identifier for your new module.
-
Position of the module: Here, the module should be placed at the
topof the main module, if possible. If several modules are declared at the same position, the last one wins. The following positions are possible:top: the module is prepended to the top of the submodule listbottomor empty string: the module is appended to the end of the submodule listbefore:<submodulekey>: the module is inserted before the submodule identified by<submodulekey>after:<submodulekey>: the module is inserted after the submodule identified by<submodulekey>
- Path: Was used prior to TYPO3 v8, use
$modulenow and set path to null.Configuration [route Target] -
Module configuration: The following options are available:
-
access: can contain several, separated by commasystemMaintainer: the module is accessible to system maintainers only.admin: the module is accessible to admins onlyuser: the module can be made accessible per usergroup: the module can be made accessible per usergroup
- Module
iconIdentifieroricon - A language file containing
labelslike the module title and description, for building the module menu and for the display of information in the Help > About Modules module (found in the main help menu in the top bar). TheLLL:prefix is mandatory here and is there for historical reasons. - Navigation component
navigationComponentId- you can specify which navigation component you want to use, for exampleTYPO3/for a page tree orCMS/ Backend/ Page Tree/ Page Tree Element TYPO3/for a folder tree. If you don't want to show a navigation component at all you can either set this to an empty string or not declare it at all. In case the main module (e.g. "web") has a navigationComponent defined by default you'll have to also setCMS/ Backend/ Tree/ File Storage Tree Container 'inherit.Navigation Component From Main Module' => false - A
routeindicating the controller/action-combination to be called when accessing this module.Target
-
'iconIdentifier' versus 'icon'
'icon is the better and more modern way to go. It should always be used
for Core icons. Other icons however need to be registered first at the IconRegistry to
create identifiers. Note that 'icon' still works. Within custom packages it is easier
to use. Example:
'icon' => 'EXT:extkey/Resources/Public/Icons/smile.svg',Registering a toplevel module
Toplevel modules like "Web" or "File" are registered with the same API. The following example uses Extbase to register the module, however, the process for non-extbase modules is the same.
\TYPO3\CMS\Extbase\Utility\ExtensionUtility::registerModule(
'MyExtension',
'mysection',
'',
'',
[],
[
'access' => '...',
'iconIdentifier' => '...',
'labels' => '...',
]
);This adds a new toplevel module mysection. This identifier can now
be used to add submodules to this new toplevel module:
\TYPO3\CMS\Extbase\Utility\ExtensionUtility::registerModule(
'MyExtension',
'mymodule1',
'mysection',
'',
[],
[
'access' => '...',
'labels' => '...'
]
);Note
The main module name should contain only lowercase characters. Do not use an underscore or dash.
$TBE_MODULES
When modules are registered, they get added to a global array called
$GLOBALS. It contains the list of all registered
modules, their configuration and the configuration of any existing
navigation component (the components which may be loaded into the
navigation frame).
$GLOBALS can be explored using the
System > Configuration module.
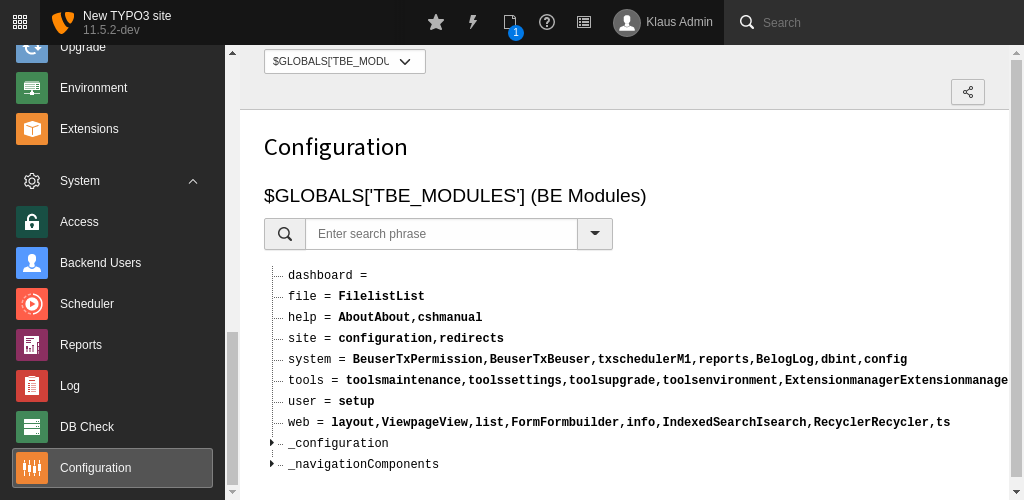
Exploring the TBE_MODULES array using the Configuration module
The list of modules is parsed by the class \TYPO3\.
