Attention
TYPO3 v11 has reached end-of-life as of October 31th 2024 and is no longer being maintained. Use the version switcher on the top left of this page to select documentation for a supported version of TYPO3.
Need more time before upgrading? You can purchase Extended Long Term Support (ELTS) for TYPO3 v11 here: TYPO3 ELTS.
Multi-factor authentication
Introduction
TYPO3 is capable of authentication via multiple factors, in short "multi-factor authentication" or "MFA". This is sometimes also referred to "2FA" as a 2-factor authentication process, where - in order to log in - the user needs
- "something to know" (= the password) and
- "something to own" (= an authenticator device, or an authenticator app on mobile phones or desktop devices).
Read more about the concepts of MFA here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-factor_authentication
TYPO3 ships with some built-in MFA providers by default. But more importantly, TYPO3 provides an API to allow extension authors to integrate their own MFA providers.
The API is designed in a way to allow providers to be used for TYPO3 backend authentication or frontend authentication with a multi-factor step in-between.
Note
Currently, TYPO3 provides the integration for the TYPO3 backend. It is planned to support multi-factor authentication for the frontend in the future.
Managing MFA providers is currently possible via the User Settings module in the tab called Account security.
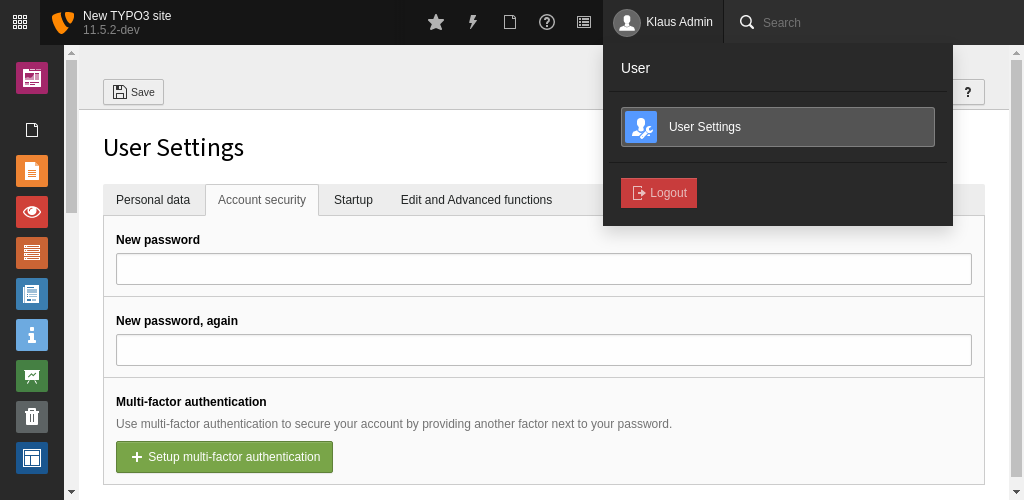
Manage your MFA providers in the User Settings module
The Account security tab displays the current state:
- whether MFA can be configured
- whether MFA is activated or
- whether some MFA providers are locked
Included MFA providers
TYPO3 Core includes two MFA providers:
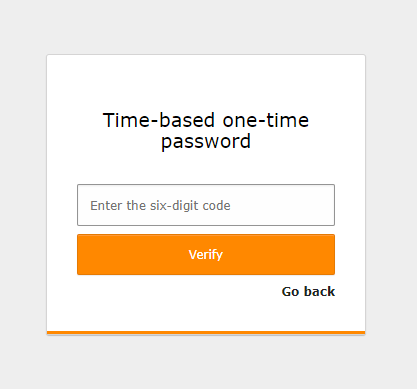
Time-based one-time password (TOTP)
TOTP is the most common MFA implementation. A QR code is scanned (or alternatively, a shared secret can be entered) to connect an authenticator app such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, 1Password, Authly, or others to the system and then synchronize a token, which changes every 30 seconds.
On each log-in, after successfully entering the password, the six-digit code shown by the authenticator app must be entered.
Recovery codes
This is a special provider which can only be activated, if at least one other provider is active. It is only meant as a fallback provider, in case the authentication credentials for the "main" provider(s) are lost. It is encouraged to activate this provider, and keep the codes at a safe place.
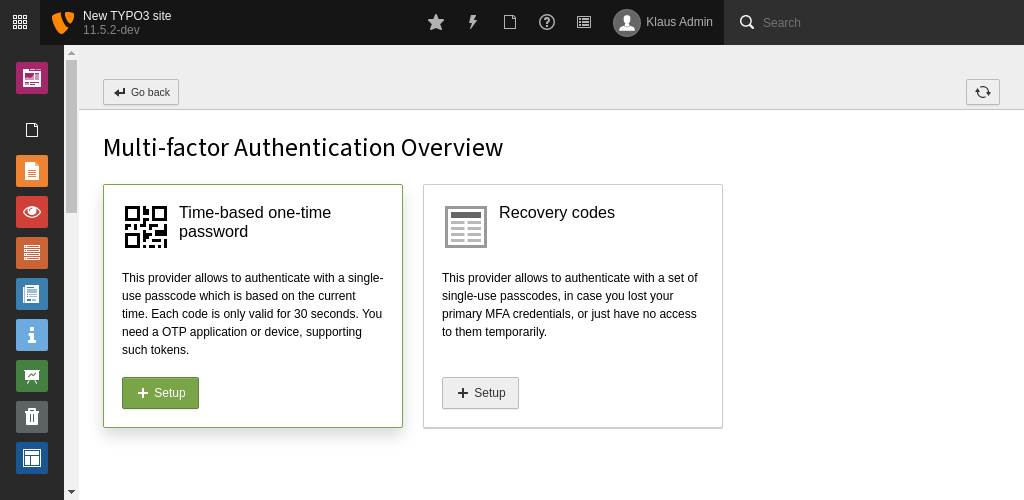
Select a MFA provider screen
Third-party MFA providers
Some third-party MFA providers are available:
Setting up MFA for a backend user
Each provider is displayed with its icon, the name and a short description in the MFA configuration module. In case a provider is active, this is indicated by a corresponding label, next to the provider's title. The same goes for a locked provider - an active provider, which can currently not be used since the provider-specific implementation detected some unusual behaviour, for example, too many false authentication attempts. Additionally, the configured default provider indicates this state with a "star" icon, next to the provider's title.
Each inactive provider contains a Setup button which opens the corresponding configuration view. This view can be different depending on the MFA provider.
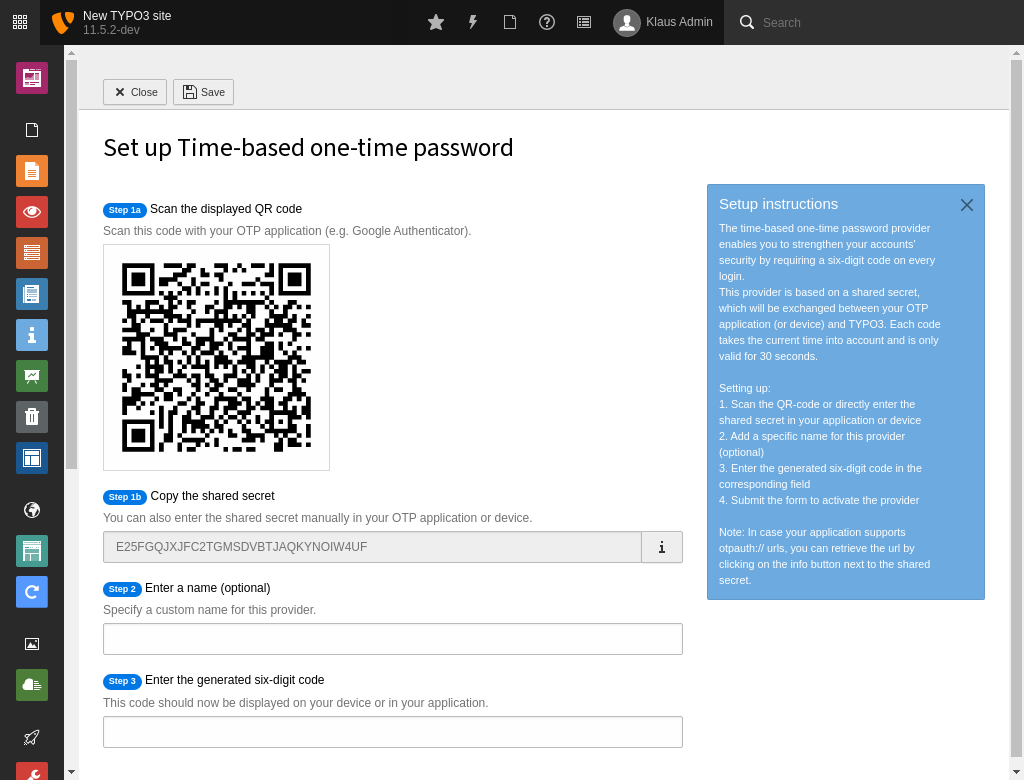
MFA TOTP provider configuration screen
Each provider contains an Edit/Change button, which allows to adjust the provider's settings. This view allows, for example, to set a provider as the default (primary) provider, to be used on authentication.
Note
The default provider setting will be automatically applied on activation of the first provider, or in case it is the recommended provider for this user.
In case the provider is locked, the Edit/Change button changes its button title to Unlock. This button can be used to unlock the provider. This, depending on the provider to unlock, may require further actions by the user.
The Deactivate button can be used to deactivate the provider. Depending on the provider, this will usually completely remove all provider-specific settings.
The "Authentication view" is displayed as soon as a user with at least one active provider has successfully passed the username and password mask.
As for the other views, it is up to the specific provider, used for the current multi-factor authentication attempt, what content is displayed in which view. If the user has further active providers, the view displays them as "Alternative providers" in the footer to allow the user to switch between all activated providers on every authentication attempt.
All providers need to define a locking functionality. In case of the TOTP and recovery code providers, this, for example, includes an attempts count. These providers are locked in case a wrong OTP was entered three times in a row. The count is automatically reset as soon as a correct OTP is entered or the user unlocks the provider in the backend.
All TYPO3 Core providers also feature the "Last used" and "Last updated" information which can be retrieved in the "Edit/Change" view.
By default, the field in the User Settings module is displayed for every backend user. It is possible to disable it for specific users via user TSconfig:
setup.fields.mfaProviders.disabled = 1Administration of user's MFA providers
If a user is not able to access the backend anymore, for example, because all of their active providers are locked, MFA needs to be disabled by an administrator for this specific user.
Administrators are able to manage the user's MFA providers in the corresponding user record. The new Multi-factor authentication field displays a list of active providers and a button to deactivate MFA for the user, or only a specific MFA provider.
Note
All of these deactivate buttons are executed immediately, after confirming the dialog, and cannot be undone.
The listing of backend users in the System > Backend Users module also displays for each user, whether MFA is enabled or currently locked. This allows an administrator to analyze the MFA usage of their users at a glance.
The System > Configuration admininistration module shows an overview of all currently registered providers in the installation. This is especially helpful to find out the exact provider identifier, needed for some user TSconfig options.
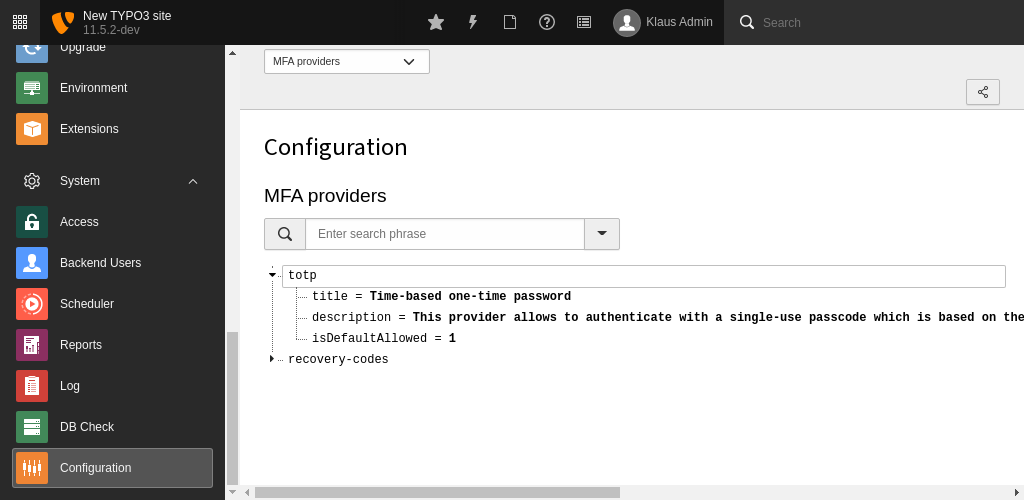
MFA providers in the configuration module
Configuration
Enforcing MFA for users
It seems reasonable to require MFA for specific users or user groups. This can be achieved with $GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['BE']['requireMfa'] which allows four options:
0- Do not require multi-factor authentication (default)
1- Require multi-factor authentication for all users
2- Require multi-factor authentication only for non-admin users
3- Require multi-factor authentication only for admin users
To set this requirement only for a specific user or user group, a user TSconfig
option auth. is available.
The user TSconfig option overrules the global configuration.
auth.mfa.required = 1Allowed provider
It is possible to only allow a subset of the available providers for some users or user groups.
A configuration option "Allowed multi-factor authentication providers" is available in the user groups record in the "Access List" tab.
There may be use cases in which a single provider should be disallowed for a specific user, which is configured to be allowed in one of the assigned user groups. Therefore, the user TSconfig option auth.mfa.disableProviders can be used. It overrules the configuration from the "Access List": if a provider is allowed in "Access List" but disallowed via user TSconfig, it will be disallowed for the user or user group the TSconfig applies to.
This does not affect the remaining allowed providers from the "Access List".
auth.mfa.disableProviders := addToList(totp)Recommended provider
To recommend a specific provider,
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['BE']['recommendedMfaProvider']
can be used and is set to totp (time-based one-time password) by default.
To set a recommended provider on a per user or user group basis, the user TSconfig option auth.mfa.recommendedProvider can be used, which overrules the global configuration.
auth.mfa.recommendedProvider = totpTYPO3 integration and API
To register a custom MFA provider, the provider class has to implement the
EXT:core/Classes/Authentication/Mfa/MfaProviderInterface.php (GitHub), shipped via a
third-party extension. The provider then has to be configured in the extension's
Services. or Services. file with the
mfa.
tag.
services:
# Place here the default dependency injection configuration
MyVender\MyExtension\Authentication\Mfa\MyProvider:
tags:
- name: mfa.provider
identifier: 'my-provider'
title: 'LLL:EXT:my_extension/Resources/Private/Language/locallang.xlf:myProvider.title'
description: 'LLL:EXT:my_extension/Resources/Private/Language/locallang.xlf:myProvider.description'
setupInstructions: 'LLL:EXT:my_extension/Resources/Private/Language/locallang.xlf:myProvider.setupInstructions'
icon: 'tx-myextension-provider-icon'
Read how to configure dependency injection in extensions.
This will register the provider
My with the
my-
identifier. To change the position of your provider the
before and
after arguments can be useful. This can be needed, for example, if you
like your provider to show up prior to any other provider in the MFA
configuration module. The ordering is also taken into account in the
authentication step while logging in. Note that the user-defined default
provider will always take precedence.
If you do not want your provider to be selectable as a default provider, set the
default argument to false.
You can also completely deactivate existing providers with:
services:
# Place here the default dependency injection configuration
TYPO3\CMS\Core\Authentication\Mfa\Provider\TotpProvider: ~
The
Mfa contains a lot of methods to be implemented by
the providers. This can be split up into state-providing ones, for example,
is or
is, and functional ones, for example,
activate or
update.
Their exact task is explained in the corresponding PHPDoc of the interface files and the Core MFA provider implementations.
All of these methods are receiving either the current
PSR-7 request object, the
\TYPO3\ or both.
The
Mfa can be used to retrieve and update the
provider-specific properties and also contains the
get method,
providing the current user object.
To store provider-specific data, the MFA API uses a new database field
mfa,
which can be freely used by the providers. The field contains a JSON-encoded
array with the identifier of each provider as array key. Common properties of
such provider array could be active or last. Since the information is
stored in either the
be_ or the
fe_ table, the context
is implicit. Same goes for the user the providers deal with. It is important to
have such a generic field so providers are able to store arbitrary data, TYPO3
does not need to know about.
To retrieve and update the providers data, the already mentioned
Mfa, which is automatically passed to all
necessary provider methods, should be used. It is highly discouraged
to directly access the
mfa database field.
