Attention
TYPO3 v11 has reached end-of-life as of October 31th 2024 and is no longer being maintained. Use the version switcher on the top left of this page to select documentation for a supported version of TYPO3.
Need more time before upgrading? You can purchase Extended Long Term Support (ELTS) for TYPO3 v11 here: TYPO3 ELTS.
Backend layout
Backend layouts can be defined as database records or via page TSconfig. Page TSconfig should be preferred as it can be stored in the file system and be kept under version control.
Backend layout video
Benjamin Kott: How to implement frontend layouts in TYPO3 using backend layouts
Backend layout configuration
The backend layout to be used can be configurated for each page and/or a pages' subpages in the Page properties > Appearance. Multiple backend layouts are available if an extension providing backend layouts is installed or backend layouts have been defined as records or page TSconfig.
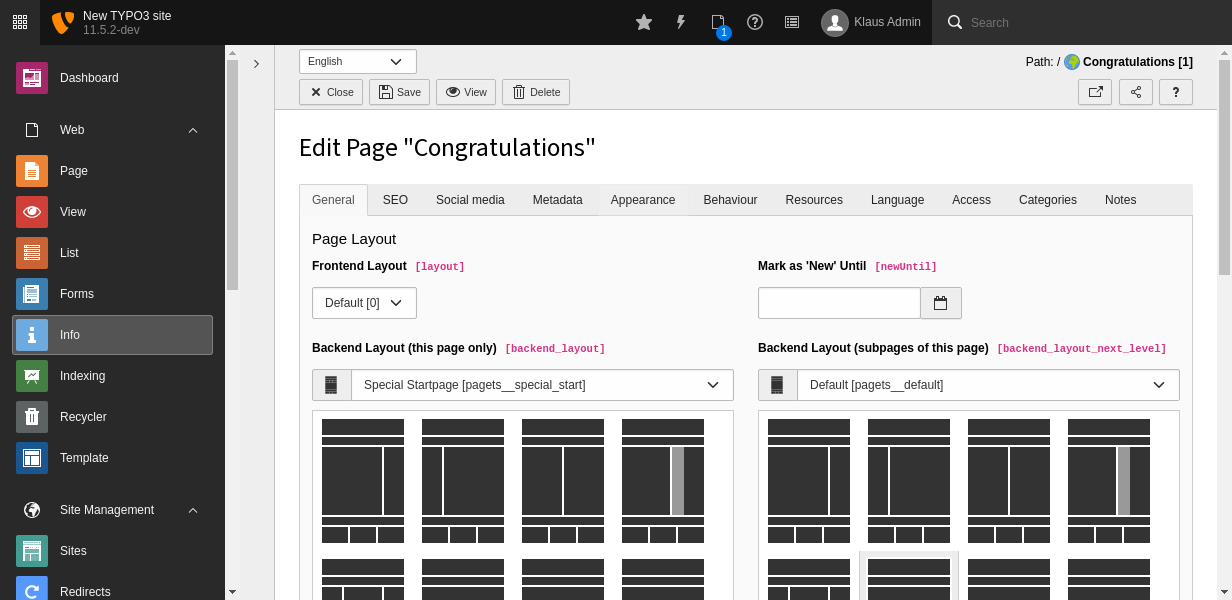
Choose the backend layout in the page properties
The Info module gives an overview of the backend layouts configured or inherited from a parent page at Web > Info > Pagetree overview > Type: Layouts:
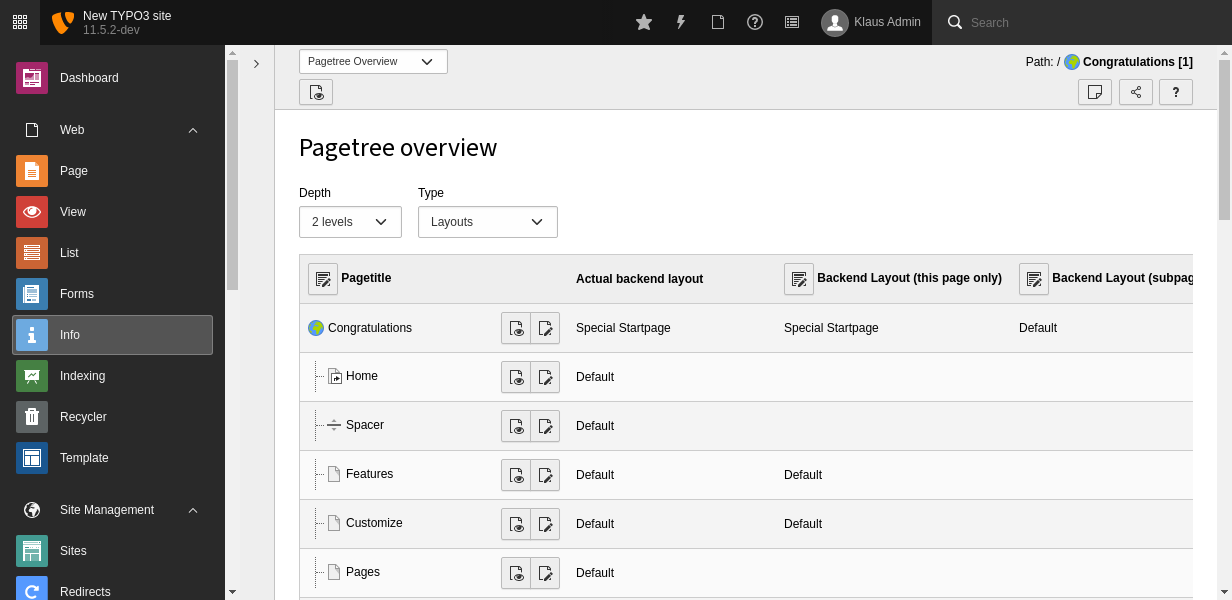
Overview of the backend layouts used
Backend layout definition
Backend layouts can be configured either as "backend layout" record in a sysfolder or as page TSconfig entry in
mod.. Each layout will be saved with a key. The "backend layout" records are
using their uid as a key, therefore layouts defined via page TSconfig should use a non-numeric string key. It is a good
practice to use a descriptive name as key.
The entries title and icon are being used to display the backend layout options in the page properties.
The overall grid size will be defined by
config. and
row.
Additional rows in the
rows array and additional columns in the each rows
columns section
will be ignored when they are greater then
row or
col respectively.
Each column position can span several columns and or several rows. Each column position must have a distinct number between 0 and n. It is best practice to always assign "0" to the main column if there is such a thing as a main column. Multiple backend layouts that contain similar parts, i.e. header, footer, aside, ... should each have assigned the same number within one project. This leads to a uniform position of the content, which makes it more clear for further use.
Backend layout simple example
The following page TSconfig example creates a simple backend layout consisting of two rows and just one column.
mod {
web_layout {
BackendLayouts {
exampleKey {
title = Example
config {
backend_layout {
colCount = 1
rowCount = 2
rows {
1 {
columns {
1 {
name = LLL:EXT:frontend/Resources/Private/Language/locallang_ttc.xlf:colPos.I.3
colPos = 3
colspan = 1
}
}
}
2 {
columns {
1 {
name = Main
colPos = 0
colspan = 1
}
}
}
}
}
}
icon = EXT:example_extension/Resources/Public/Images/BackendLayouts/default.gif
}
}
}
}Backend layout advanced example
The following page TSconfig example creates a 3x3 backend layout with 5 column position sections in total. The topmost row (here called "header") spans all 3 columns. There is an "aside" spanning two rows on the right.
mod.web_layout.BackendLayouts {
exampleKey {
title = Example
icon = EXT:example_extension/Resources/Public/Images/BackendLayouts/default.gif
config {
backend_layout {
colCount = 3
rowCount = 3
rows {
1 {
columns {
1 {
name = Header
colspan = 3
colPos = 1
}
}
}
2 {
columns {
1 {
name = Main
colspan = 2
colPos = 0
}
2 {
name = Aside
rowspan = 2
colPos = 2
}
}
}
3 {
columns {
1 {
name = Main Left
colPos = 5
}
2 {
name = Main Right
colPos = 6
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}Output of a backend layout in the frontend
The backend layout to be used on a certain page gets determined either by the backend layout being chosen directly and stored in the pages field "backend_layout" or by the field "backend_layout_next_level" of a parent page up the rootline.
To avoid complex TypoScript for integrators, the handling of backend layouts has been simplified for the frontend.
To get the correct backend layout, the following TypoScript code can be used:
page.10 = FLUIDTEMPLATE
page.10 {
file.stdWrap.cObject = CASE
file.stdWrap.cObject {
key.data = pagelayout
default = TEXT
default.value = EXT:sitepackage/Resources/Private/Templates/Home.html
3 = TEXT
3.value = EXT:sitepackage/Resources/Private/Templates/1-col.html
4 = TEXT
4.value = EXT:sitepackage/Resources/Private/Templates/2-col.html
}
}Using data = pagelayout is the same as using as
field = backend_layout
ifEmpty.data = levelfield:-2,backend_layout_next_level,slide
ifEmpty.ifEmpty = defaultIn the Fluid template the column positions can be accessed now via content mapping as described here Content mapping.
Reference implementations of backend layouts
The extension bootstrap_package ships several Backend layouts as well as an example configuration of how to include frontend templates for backend layouts (see its setup.typoscript)
Extensions for backend layouts
In many cases besides defining fixed backend layouts a more modular approach with the possibility of combining different backend layouts and frontend layouts may be feasible. The extension gridelements integrates the grid layout concept also to regular content elements.
The extension content_defender offers advanced options to the column positions i.e. allowed or disallowed content elements, a maximal number of content elements.
