Managing translations in TYPO3
This section highlights the different ways to translate and manage TYPO3 language files (XLIFF 1.2 and 2.x).
Table of contents
Fetching translations or updating language packs
The backend module System > Maintenance > Manage Language Packs displays a list of available languages and can fetch or update language packs for system and extension translations from the official TYPO3 translation server.
The module is straightforward to use. Downloaded language packs are stored in the environment’s getLabelsPath().
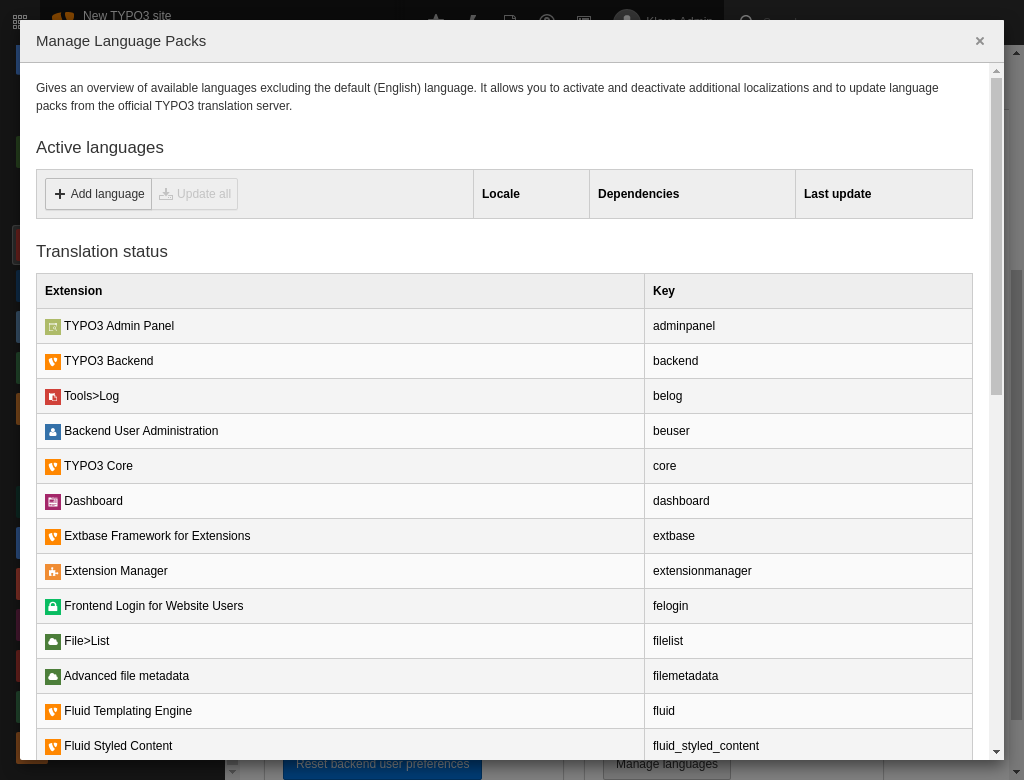
The Languages module with some active languages and status of extensions language packs
Language packs can also be fetched using the command line:
vendor/bin/typo3 language:updatetypo3/sysext/core/bin/typo3 language:updateLoading an additional language pack
Administrators can install additional language packs directly in the backend:
-
Go to System > Maintenance > Manage Language Packs
Open the backend language administration module
-
Select Add Language and activate the new language:
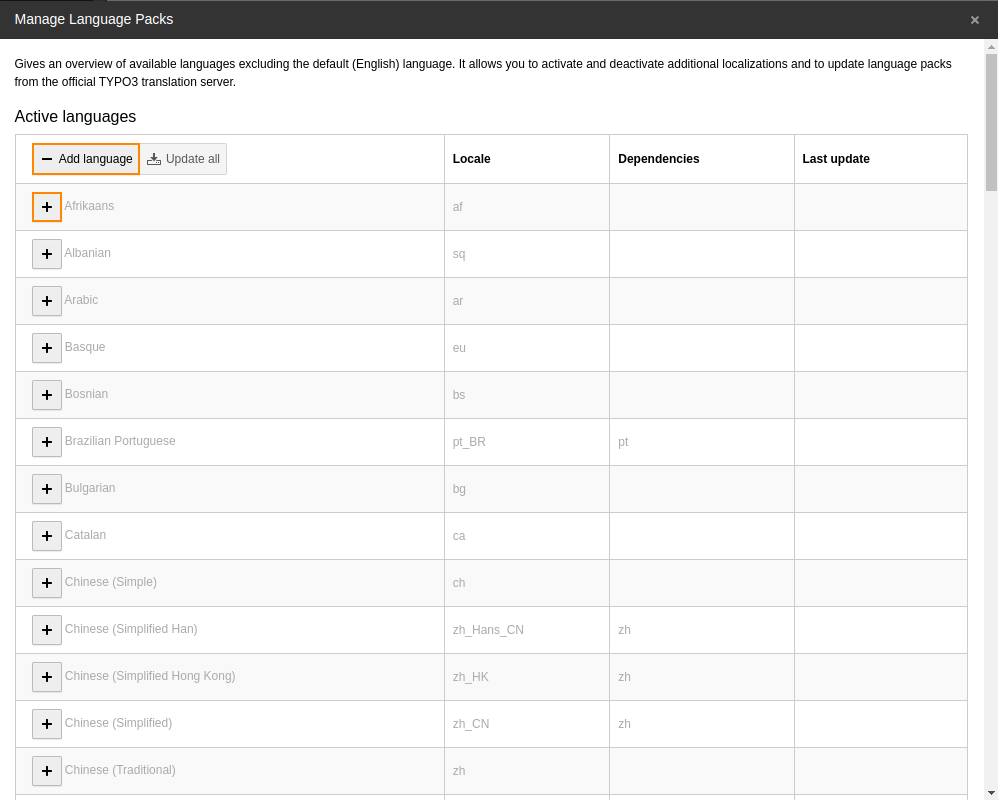
Add the desired language
-
The selected language is now available:
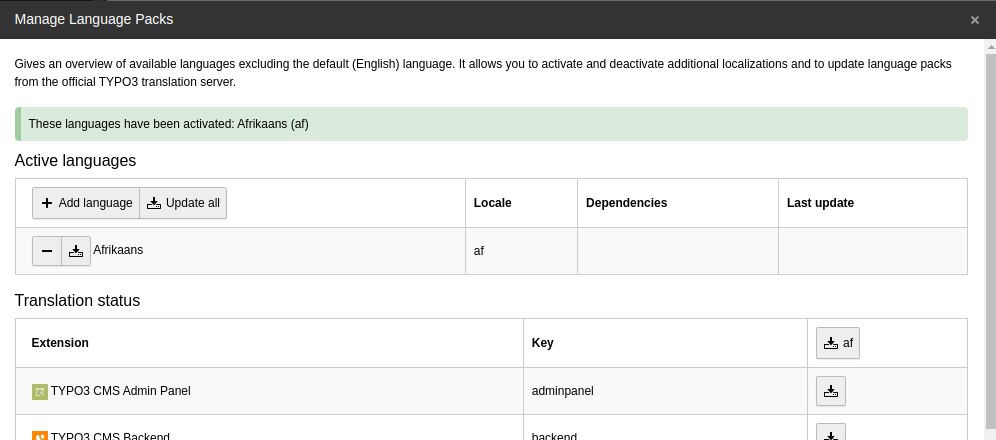
Translating XLIFF files locally
You can translate TYPO3 XLIFF files directly in your development environment using any XML or translation editor that supports the XLIFF format.
TYPO3 v14 and newer support both XLIFF 1.2 and XLIFF 2.x:
- XLIFF 2.x: uses
<unit>elements and the<target state="…">attribute (state="reviewed"/state="final"= approved) - XLIFF 1.2: uses
<trans-and theunit> approved="yes"attribute
Both formats are automatically detected and parsed by TYPO3.
You can use any text or translation editor to modify .xlf files locally.
Ensure that your chosen tool supports the XLIFF 2.x format, which is the
default for TYPO3 v14 and later.
Overriding or extending translations
Changed in version 14.0
$GLOBALS has been moved
to $GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['LANG']['resourceOverrides'].
Option $GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['LANG']['resourceOverrides'] allows overriding XLIFF files. This applies to both translations and default (language = English) files.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
defined('TYPO3') or die();
// Override a file in the default language
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['LANG']['resourceOverrides']
['EXT:frontend/Resources/Private/Language/locallang_tca.xlf'][]
= 'EXT:examples/Resources/Private/Language/custom.xlf';
// Override a German ("de") translation
$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['LANG']['resourceOverrides']['de']
['EXT:news/Resources/Private/Language/locallang_modadministration.xlf'][]
= 'EXT:examples/Resources/Private/Language/Overrides/de.locallang_modadministration.xlf';
The German language file could look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xliff version="2.0" xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:xliff:document:2.0" srcLang="en" trgLang="de">
<file id="f1">
<unit id="pages.title_formlabel">
<segment>
<source>Most important title</source>
<target state="final">Wichtigster Titel</target>
</segment>
</unit>
</file>
</xliff>
TYPO3 loads either XLIFF 1.2 or 2.x — the format is detected automatically.
The result can be seen in the backend:
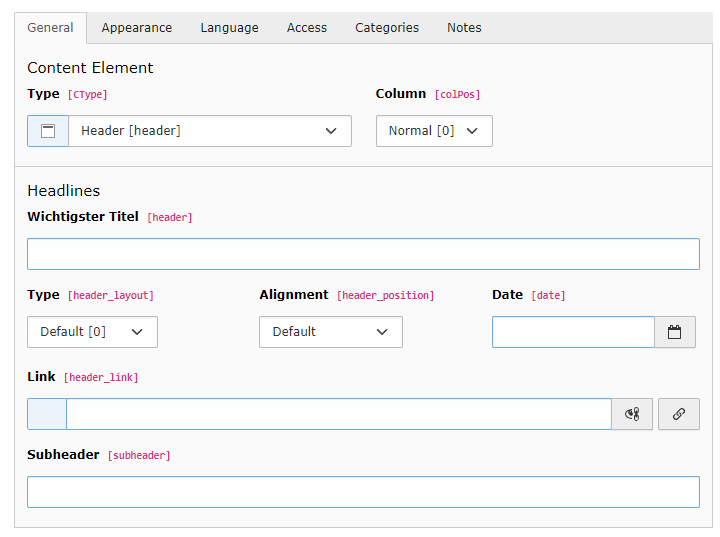
Custom translation in the TYPO3 backend
Attention
- You only need to include the labels you want to override.
- The path to the file to be overridden must be specified as
EXT:and must end withmy_ extension/... .xlf.
Attention
The following is a known limitation:
- Custom label files must be located inside an extension. Other locations are ignored.
- The original translation must exist in the environment’s
getLabelsPath() or next to the base translation file in
the extension, for example in
my_.extension/ Resources/ Private/ Language/
Adding custom languages
TYPO3 supports many languages by default, but you can also add custom languages and provide your own translations using XLIFF 1.2 or 2.x.
-
Define the language
Example: add "gsw_CH" (Swiss German) as an additional language.
config/system/additional.php | typo3conf/system/additional.php$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['localization']['locales']['user'] = [ 'gsw_CH' => 'Swiss German', ];Copied! -
Add fallback to another language
This language does not have to be translated completely. It can fall back to another language so that only differing labels need translation.
config/system/additional.php | typo3conf/system/additional.php$GLOBALS['TYPO3_CONF_VARS']['SYS']['localization']['locales']['dependencies'] = [ 'gsw_CH' => ['de_AT', 'de'], ];Copied!In this example, "gsw_CH" falls back to "de_AT" and then to "de".
-
Add translation files
Translation files for system and extension labels must be stored under the correct subfolder of the environment’s getLabelsPath(). The minimum requirement is to translate the language name so it appears in the user settings.
gsw_CH/setup/Resources/Private/Language/gsw_CH.locallang.xlf<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xliff version="2.0" xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:xliff:document:2.0" srcLang="en" trgLang="gsw_CH"> <file id="f1"> <unit id="lang_gsw_CH"> <segment> <source>Swiss German</source> <target state="final">Schwiizertüütsch</target> </segment> </unit> </file> </xliff>gsw_CH/setup/Resources/Private/Language/gsw_CH.locallang.xlf<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xliff xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:xliff:document:1.2" version="1.2"> <file source-language="en" target-language="gsw_CH" datatype="plaintext" original="EXT:setup/Resources/Private/Language/locallang.xlf"> <body> <trans-unit id="lang_gsw_CH" approved="yes"> <source>Swiss German</source> <target>Schwiizertüütsch</target> </trans-unit> </body> </file> </xliff>The new language is now available in the backend user settings:
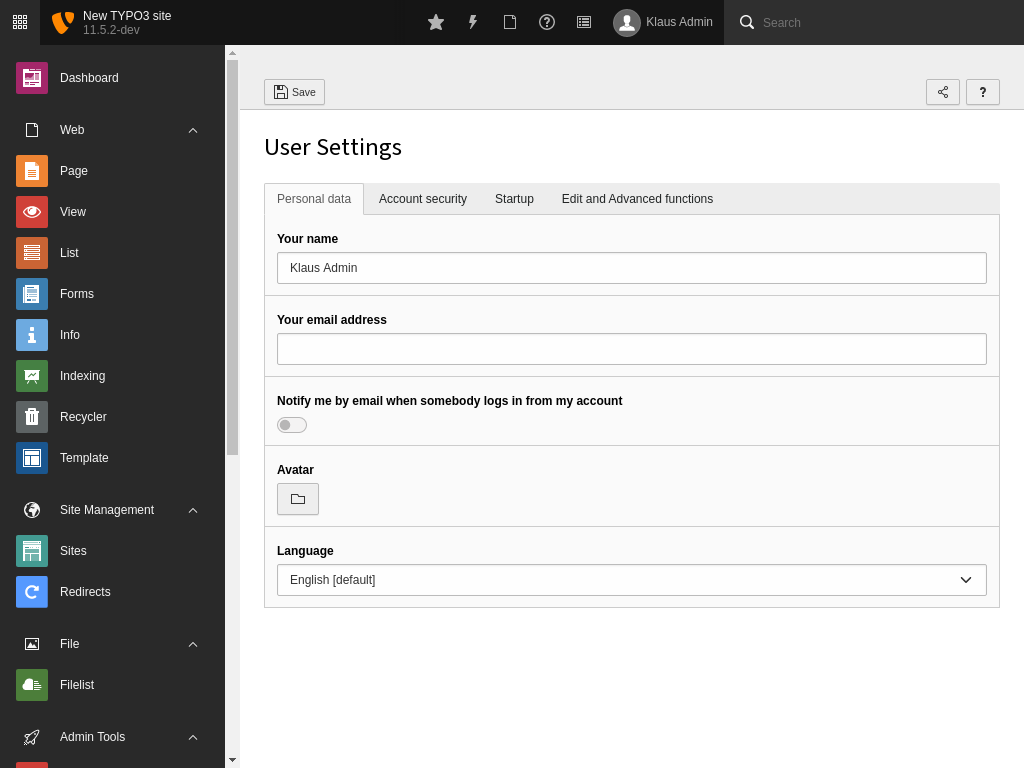
The new language appears in the user preferences
For your own extensions, provide the custom language files in the
Resources/folder, for examplePrivate/ Language/ gsw_.CH. locallang_ db. xlf
Each language always falls back on the default one (English) if no translation is found. A custom language automatically falls back on its defined dependencies. For example, "de_AT" would fall back on "de" automatically.
See also
Configure
typo3Language to use custom languages in the frontend.
See Adding Languages for details.
