Secure file permissions (operating system level)
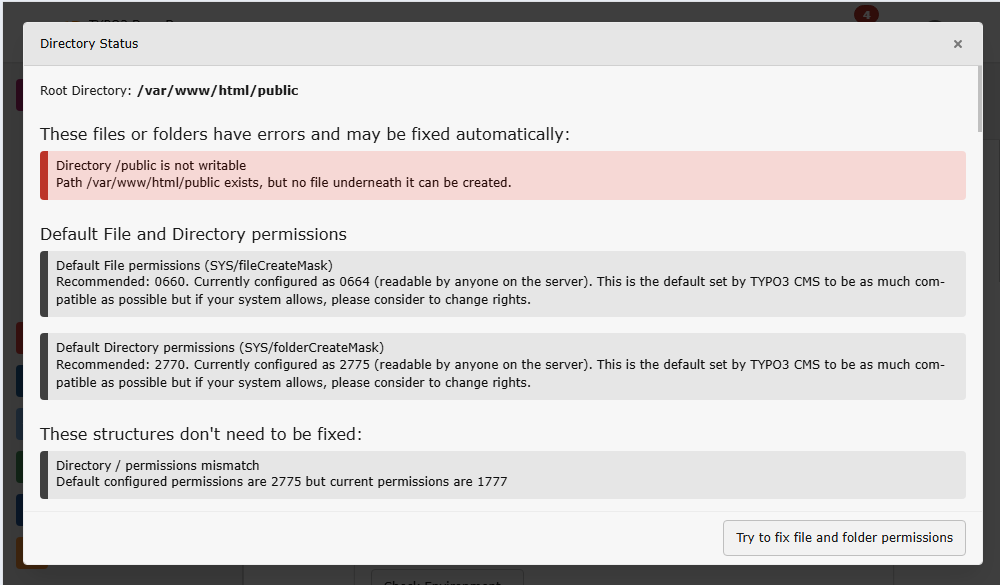
The tool "Directory Status" in System > Environment displays warnings about missing write permissions
This chapter explains how to securely configure file and directory permissions at the operating system level for TYPO3 installations. It focuses on who can read and write to files on disk.
To learn how to prevent public access via the web server, see Restrict public file access in the web server.
A common risk is allowing one user to read or modify another client's files—
especially in shared environments. A misconfigured server where all sites run
as the same user can allow cross-site scripting, data theft, or manipulation of
TYPO3 files such as config/.
TYPO3 can be installed either in classic (non-Composer) mode or using a Composer-based setup. Each approach requires a slightly different file permission strategy.
Table of contents
Composer-based installations
In Composer-based TYPO3 installations, the document root is typically a
public/ directory. Core files, extensions, and the vendor/ directory
reside outside the web root, improving security by design.
Recommendations:
- Set the web server's document root to
public/only. -
Grant the web server user write access to:
public/fileadmin/ public/typo3temp/ var/(used for cache, logs, sessions, etc.)
- The
public/_directory must be readable by the web server. It is generated during deployment or Composer operations and should not be writable at runtime.assets/ -
The
config/directory should be read-only for the web server in production environments unless certain TYPO3 features require write access:- To allow changing site configurations via the backend, the web server needs
write access to
config/.sites/ - To allow system maintainers to update settings via the
System > Settings module, the web server needs write
access to
config/.system/ settings. php
- To allow changing site configurations via the backend, the web server needs
write access to
- Keep
vendor/,composer., andjson public/read-only for the web server.index. php
Classic-mode installations
In classic TYPO3 installations, all TYPO3 files (Core, extensions, uploads) are located inside the web server's document root. This increases the risk of file exposure or accidental manipulation, making secure filesystem permissions essential.
Recommendations:
- On shared hosting, ensure each virtual host runs under a separate system user.
- Revoke write access for the web server user to the TYPO3 core source directories,
especially
typo3/(core system extensions) andsysext/ vendor/ -
Allow write access only to:
fileadmin/typo3temp/- Only grant write access to subdirectories within
typo3conf/as needed: typo3conf/,ext/ typo3conf/,autoload/ typo3conf/: Required if you want to install or update extensions using the Extension Manager.Package States. php typo3conf/: Stores site configuration; writable if managing sites through the backend.sites/ typo3conf/: Stores system settings; writable if modifying settings via the System > Settings module.system/ typo3conf/: Must be writable to allow downloading or updating translation files via the module System > Maintenance > Manage Language Packs.l10n/
- The rest of the
typo3conf/directory should remain read-only to the web server where possible. - On UNIX/Linux systems, enforce appropriate user/group ownership and permissions
(e.g.,
chmod,chown).
Check file permissions in the backend
TYPO3 provides a built-in backend tool to verify directory permissions.
You can access it via:
System > Environment > Directory Status
This view lists key directories such as fileadmin/, config/,
var/, and others, and shows whether the current web server user has
the recommend level of access.
Use this tool to confirm that required directories are writable after deployment or when debugging permission-related issues.
